Man calls himself "the king of nature," and one must admit that there is a significant amount of truth in this. For some fifty thousand years we have traveled an impressive way from animal skins and a stone ax to a nuclear reactor and space flights. Despite the undoubted achievements, the modern man is as helpless before the power of the elements as his distant Cro-Magnon ancestor. The forces of nature are so great that before them all the power of our technologies is powerless.
Hundreds and thousands of various natural disasters, dangerous and emergency situations occur on Earth annually: hurricanes, tornadoes, fires, floods, earthquakes, etc. A large number of people become their victims. Moreover, human economic activity itself is a source of serious potential danger. Its result is often man-made emergencies that can exceed any hurricanes or earthquakes in their consequences. As an example, Fukushima or Chernobyl.
Even more dangers and destruction are wars, which are in themselves a terrible disaster. In addition to the dangers arising from the conduct of hostilities, they lead to refugee flows and real humanitarian disasters, mainly from which the civilian population suffers. Since the beginning of the 1990s, 38 local military conflicts and 41 small wars have occurred in the world.
It is not always possible to understand the causes of emergency situations or to prevent them, but to deal with the consequences of the rampant elements and help the victims of it we are not only capable, but obliged. In each country there is a special structure (or several), whose tasks include the elimination of the consequences of emergency situations, as well as assistance in emergency situations to the civilian population.

In our country, such duties are performed by the Ministry of Emergency Situations (MES) of the Russian Federation. The decision to introduce or not the state of emergency in a certain territory is made by the Government of the Russian Federation, the Emergencies Ministry or special commissions. The work of special services, government agencies, local governments, and other institutions and organizations in emergency situations is regulated by federal law (FZ) "On the Protection of the Population and Territories from Emergencies".
What is an emergency?
An emergency situation (ES) is a situation that has developed in a certain area as a result of a man-made accident, a natural phenomenon, or a natural disaster. As a rule, it is a threat to the life and health of people, destroys material values, damages the natural environment and the national economy.

The media often uses the term "extreme situation" (ES), which denotes various incidents: accidents, fires, abnormal situations at work, etc. In these situations (ES and ES), there is much in common, however, ES is much more significant in scale than serious consequences.
In the descriptions of emergency situations the words "accident", "catastrophe" are found, and they are used as synonyms. This is not entirely correct. Accident - an emergency situation associated with the technique or mechanisms. For example, a breakdown of a production line, a vehicle crash, a leak of chemicals. The magnitude of such incidents varies greatly. A catastrophe is a broader term; it denotes a tragic accident with considerable damage and, as a rule, with massive defeat and death.
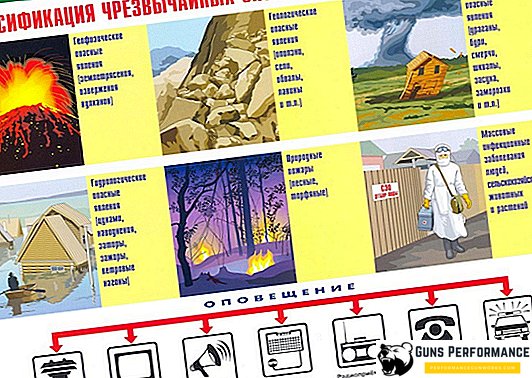
Existing classifications of emergency situations
Currently, there are several classifications of emergency situations. Based on the nature of the causes of emergencies, they can be divided into two large groups:
- conflict;
- conflict-free.
The first group includes all types of emergencies caused by military actions, conflicts on religious and national grounds, terrorist acts, rampant criminality, revolutions, riots, etc. These are emergency situations caused by destructive human actions or conflicts between groups of people. Emergencies of the second type include accidents and disasters in industry and natural emergencies, as well as environmental disasters.
Emergencies are unintentional and intentional. In the latter case, it is usually about the attacks.
The most important factor by which an emergency situation is classified and assessed is its scale and extent of damage caused by an emergency. The consequences of emergency situations are assessed here: the size of the lesion, the losses among the population, the damage to infrastructure and the environment. This aspect is very important for planning and carrying out rescue and other work.
Damage from emergencies can be direct and indirect (indirect). The first type includes the cost of destruction and damage, damage from the failure of business facilities, damage to natural resources, disability of workers due to injury. Indirect damage: economic losses due to cessation of economic activity, the costs of eliminating the consequences of emergency situations, social security of the population affected by the state of emergency, etc. Often, indirect damage is much more direct and can have a negative impact on the economy of a country for decades.
Based on the classification according to the degree of damage, emergencies are:
- Local character. In this case, the emergency zone does not extend beyond the territory of the facility where the incident occurred. The death toll does not exceed ten people, and the damage - 100 thousand rubles;
- Municipal character. The emergency zone does not go beyond the boundaries of a settlement or a city of federal significance. The number of victims does not exceed 50 people, and the amount of damage is 5 million rubles;
- Intermunicipal. In such an emergency, the affected area extends to several localities, the number of victims exceeds 50 people, and the material damage amounts to more than 5 million rubles;
- Regional nature. The number of victims is over 50, but not more than 500 people, and the amount of damage is more than 5 million rubles, but does not exceed 500 million rubles. In this emergency situation does not go beyond the boundaries of one subject of the Russian Federation;
- Interregional nature. In this case, the emergency zone affects several federal subjects at once, the number of victims is not more than 500 people, and the damage does not exceed 500 million rubles;
- Federal character. This group includes an emergency situation, as a result of which the number of victims exceeds 500 people or the amount of material damage is more than 500 million rubles.
There are also transboundary emergencies where, for example, an accident or catastrophe occurs outside the Russian borders, but the damaging factors have a detrimental effect on our territory. Several years ago, a Chinese enterprise leaked poisonous substances, which then fell into the Russian part of Amur.
Also, peacetime emergencies are classified according to the nature of the striking action (emergency factor). This moment is very important, because it is the nature of the source of the emergency that determines the nature of the conduct of rescue and other urgent measures in the disaster zone. The source of the disaster can be:
- thermal;
- mechanical;
- biological;
- radiation;
- chemical.
By the nature of the occurrence of emergency situations are divided into:
- natural;
- man-made;
- environmental;
- social;
- combined.
According to the speed of development of events, emergency situations are:
- sudden - earthquakes, explosions, traffic accidents;
- rapid - fires, emissions of radioactive or toxic substances;
- moderate - floods, volcanic eruptions.
Natural Emergencies: General Description and Features
The most extensive class of emergencies, which includes disasters caused by the elemental forces of nature. This group includes earthquakes, droughts, tornadoes, mudflows, dust storms, hurricanes, avalanches in the mountains, volcanic eruptions and much more. It is so numerous that for convenience it has been divided into several subgroups.
For example, there are emergencies caused by hydrometeorological phenomena, such as strong wind, too heavy rainfall, snowfall, drought, etc. The Roshydrometcenter is dealing with an emergency of this type in our country.

Climatic natural phenomena - the most frequent culprit in the occurrence of emergencies on the planet. Moreover, it is they who are responsible for the majority of the victims who fall into natural emergencies. According to the UN, this figure reaches 90%.
The second type of natural emergency is dangerous geophysical phenomena, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. They have no equal in destructive capacity. A strong earthquake could well destroy a large city, causing the death of hundreds of thousands of people. Volcanoes have no less destructive power - the fate of the Roman city of Pompeii is clear evidence of this.
Unfortunately, we can not yet confidently predict such destructive natural phenomena, therefore, the protection of the population and territories from emergency situations of this type is very difficult. It remains only to deal with their consequences. Almost 40% of the territory of Russia belongs to the zone of increased seismic hazard, and 9% of earthquakes of magnitude up to 7-8 may occur.
Another dangerous subgroup of natural emergencies is geological emergencies. These include landslides, mudflows, subsidence of soil, avalanches, dust storms.
In a separate subgroup of natural emergencies include various marine natural phenomena: typhoons, tsunamis, strong storms, intense ice drift. It is clear that such emergencies are dangerous for coastal areas, in addition, they cause significant damage to shipping and marine fisheries.

Also, natural emergencies include massive damage to farm animals and plants by various diseases or pests. These emergency situations do not lead to the death of people and the destruction of material objects, but they are fraught with significant economic losses. Veterinary services are involved in the prevention and control of such emergency situations of this type.
A natural emergency for Russia of a natural character is forest fires. This is facilitated by vast areas of forest in our country. From 10 to 30 thousand fires of various size and complexity are recorded annually. They cause enormous damage to the country's economy.
Man-made emergencies, their description and features
Emergencies related to emergency situations at various technical facilities: factories, power plants, pipelines, storage facilities, transport, etc., are man-made. This group is also quite numerous and heterogeneous. It includes various types of emergencies, differing both in their character (damaging factors) and in scale.
The most difficult and dangerous are accidents that can lead to the release of toxic chemical or radioactive substances. Such incidents pose a significant threat to human health and the environment. No less dangerous leaks of biohazardous substances.

The man-made emergencies include accidents in transport, fires at industrial facilities, the collapse of buildings and structures.
Emergencies associated with the critical infrastructure of human settlements are especially dangerous: accidents of power grids, urban wastewater treatment plants, heating networks, etc. Modern people are very dependent on all this, turning off electricity in a big city for at least a day completely disrupts the normal rhythm of its life. Such emergencies are not uncommon.
Another type of dangerous man-made emergencies is accidents at hydraulic structures: dams, dams. They can lead to numerous casualties and the flooding of large areas.
Environmental emergencies and their impact on flora and fauna
Ecological emergencies - the creation of a situation in a certain territory, which adversely affects the flora and fauna, as well as the general state of the aquatic and air environment. The cause of this type of emergency can be a serious technogenic accident or a natural disaster, an ineffective (or even simply barbaric) human economic activity.

An example of a man-made accident that led to the emergence of environmental emergencies can serve as the tragic events at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, the result was the alienation of vast territories. However, the thoughtless attitude of man to nature leads to disasters and emergency situations more often than accidents. For example, subsoil production causes subsidence of soil, landslides and landslides, and deforestation reduces biodiversity and causes mudflows and flooding. Large-scale emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere can seriously increase the level of the oceans and flood coastal areas.
Social emergencies
This type of emergency occurs as a result of a sharp conflict between social groups. The causes of such a disaster are completely different: political or religious contradictions, the difficult economic situation in the country, social injustice. Social emergencies include revolutions, street riots, armed conflicts.

Often, social emergencies also include terrorism, which is considered a peculiar form of political struggle. The consequences of terrorist attacks are very serious, and they not only cause material damage and kill innocent people, but also create an atmosphere of fear and mistrust in society. Currently, the problem of global terrorism is very acute, it can be called one of the main challenges of modern civilization.
To prevent terrorist attacks or eliminate their consequences, internal troops and other military units may be involved.
It is rather difficult to prevent social emergencies, since the reasons for their occurrence are very subjective and not always clear. To eliminate and prevent social upheavals, serious complex work of special services, politicians, doctors, psychologists, and the media is necessary. Poverty, unemployment, lack of prospects, inequality and lawlessness - this is the breeding ground for various social explosions and civil strife.
Combined emergency situations
An emergency of this type is a combination of emergency situations of several types described at once, which are observed in a certain area. Moreover, the combinations are different. Very often, man-made or natural emergencies lead to mass unrest or even armed conflict. For example, one of the prerequisites for the commencement of unrest in Syria, which later grew into a civil war, was a considerable drought, which led to a shortage and increase in the cost of food. Similar stories often happened in the past: the immediate cause of the revolution of 1917 in Russia was interruptions in the supply of grain to St. Petersburg.
Man-made accidents often lead to environmental disasters, protests and riots are often observed in areas affected by the conduct of hostilities.
The combined nature of an emergency greatly complicates the protection of the population and territories from emergency situations and the elimination of its consequences.
Principles of protection of the population in emergency situations
How to protect citizens and minimize damage from an emergency? Is there a single universal recipe for protecting the population from disasters and disasters that are so different in their nature? And to whom are the functions of dealing with emergency situations?
In our country, the state policy in the field of protection of the population from emergency situations is carried out by a special structure - the Ministry of Emergency Situations. Данное министерство проводит нормативно-правовое регулирование в этой области, а также осуществляет надзор и контроль в сфере гражданской обороны. Это военизированная организация, которой позволено приобретать и использовать оружие.

В 1995 году для противодействия стихийным бедствиям и чрезвычайным ситуациям была создана РСЧС - единая система предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций. В ее состав входят ресурсы и силы центральных органов власти, субъектов РФ и органов местного самоуправления, организаций, которые занимаются вопросом защиты территорий и населения от ЧС.
РСЧС нацелена на выполнение двух функций:
- предупреждение бедствий и снижение возможного ущерба от ЧС;
- ликвидация последствий чрезвычайных ситуаций и проведение аварийно-спасательных и других необходимых работ в зоне ЧС.
Система предупреждения и ликвидации ЧС имеет иерархическую структуру, она разделена на несколько уровней. На каждом из них созданы органы управления, силы и средства для решения необходимых задач и проведения мероприятий по защите населения и территорий.
Важнейшим элементом предупреждения чрезвычайных ситуаций и борьбы с их последствиями является гражданская оборона (ГО). Это целый комплекс мероприятий по защите населения и материальных ценностей от опасностей, возникающих в результате военных действий или же техногенных аварий и природных ЧС. Гражданскую оборону можно назвать одной из важнейших функций любого государства, которое по своему значению не уступает поддержке адекватной обороноспособности страны.

В задачи гражданской обороны входит:
- оповещение населения о возможной угрозе нападения противника, применения им ОМП, техногенных авариях, стихийных бедствий и порядке действий в подобных ситуациях;
- подготовка укрытий и защитных сооружений;
- обеспечение населения средствами индивидуальной защиты;
- при необходимости служба гражданской обороны организует эвакуацию населения в безопасные районы;
- обеспечение защиты запасов продовольствия, систем водоснабжения, сельскохозяйственных животных от заражения ядовитыми и радиоактивными веществами, а также биологическими средствами;
- обучение населения способам защиты в чрезвычайных ситуациях;
- силы ГО обязаны иметь заблаговременный план защиты той или иной территории.
Структура ГО построена по производственному и территориальному принципу. Руководитель любого предприятия является и начальником его гражданской обороны. Аналогичное правило действует и для административно-территориальных образований. Руководитель ГО несет ответственность за готовность территории или объекта противостоять чрезвычайным ситуациям, авариям и стихийным бедствиям.
Наш мир - очень опасное и непредсказуемое место. Человек обязан помнить об этом и быть готовым в любой момент противостоять грозным силам природы или машинам, вышедшим из-под его подчинения. В этом вопросе работа государственных экстренных служб, безусловно, очень важна, но куда большее значение имеет наша способность встретиться лицом к лицу с разыгравшейся стихией.












