The outer space surrounding us is not just lonely stars, planets, asteroids and comets glistening in the night sky. Cosmos is a huge system where everything is in close interaction with each other. Planets are clustered around stars, which in turn form clusters or nebulae. These formations can be represented by single luminaries, or they can number hundreds, thousands of stars, forming already larger-scale universe formations - galaxies. Our stellar country, the Milky Way galaxy, is only a small part of the vast universe, in which besides this there are other galaxies.

The universe is constantly in motion. Any object in space is part of a particular galaxy. Following the stars, galaxies also move, each of which has its own dimensions, a certain place in the dense universal order and its own trajectory of motion.
Man has managed to count the number of stars in the sky, but to determine how many galaxies in the Universe is a daunting task, both technically and theoretically.
What is the real structure of the universe?
For a long time, scientific representations of mankind about the cosmos were built around the planets of the solar system, the stars and black holes inhabiting our star house - the Milky Way galaxy. Any other galactic object detected in space by telescopes was automatically entered into the structure of our galactic space. Accordingly, there was no idea that the Milky Way is not the only universal education.

Limited technical capabilities did not allow us to glance further, beyond the Milky Way, where, according to established opinion, emptiness begins. Only in 1920, the American astrophysicist Edwin Hubble was able to find evidence that the Universe is much larger and, along with our galaxy, there are other large and small galaxies in this vast and boundless world. The real boundary of the universe does not exist. Some objects are close enough to us, only a few million light years from Earth. Others, on the contrary, are located in the far corner of the universe, being out of sight.
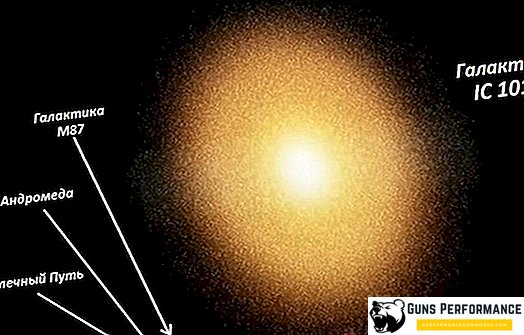
Almost a hundred years have passed and the number of galaxies today is already estimated at hundreds of thousands. Against this background, our Milky Way does not look so huge, if not to say, very tiny. Today, galaxies have already been discovered, the size of which is difficult even to mathematical analysis. For example, the largest galaxy in the Universe, IC 1101, has a diameter of 6 million light years and consists of more than 100 trillion stars. This galactic monster is located more than a billion light years from our planet.
The structure of such a huge formation, which is the universe on a global scale, is represented by emptiness and interstellar formations - fibers. The latter, in turn, are divided into superclusters, intergalactic clusters and galactic groups. The smallest link of this huge mechanism is the galaxy, represented by numerous star clusters - arms and gas nebulae. It is assumed that the Universe is constantly expanding, thus causing galaxies to move with great speed in the direction from the center of the Universe to the periphery.
If we imagine that we are observing the cosmos from our Milky Way galaxy, which is supposedly located in the center of the universe, then the large-scale model of the structure of the Universe will look like this.
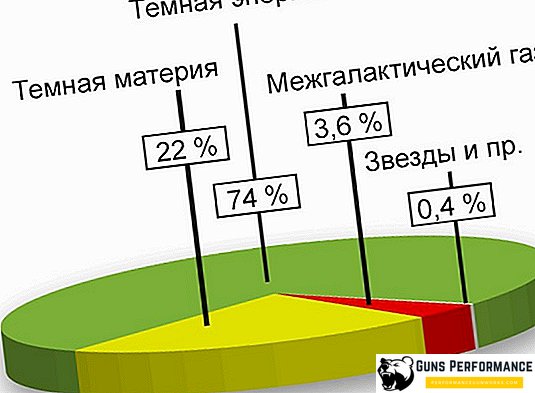
Dark matter - it is the void, superclusters, clusters of galaxies and nebula - these are all the consequences of the Big Bang, which initiated the formation of the Universe. For a billion years, its structure is transformed, the shape of galaxies changes, as some stars disappear, are absorbed by black holes, and others, on the contrary, are transformed into supernovae, becoming new galactic objects. Billions of years ago in the arrangement of galaxies was quite different than what we are seeing now. Anyway, against the background of constant astrophysical processes occurring in space, it is possible to draw certain conclusions about the fact that our Universe has a non-permanent structure. All space objects are in constant motion, changing their position, size and age.

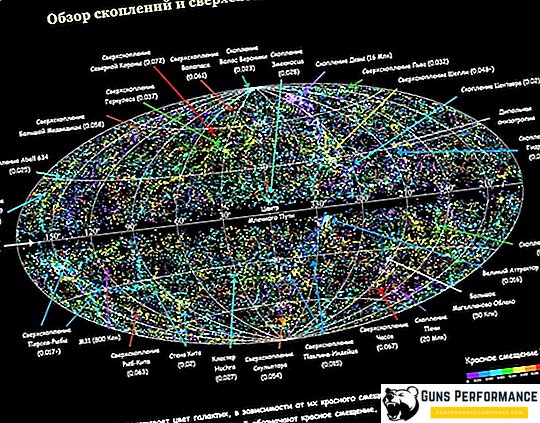
Today, thanks to the Hubble telescope, we were able to locate the closest galaxies to us, establish their size and determine the relative position of our world. By the efforts of astronomers, mathematicians and astrophysicists a map of the Universe has been compiled. Single galaxies have been identified, but for the most part, such large universe objects are grouped in several dozen groups. The average size of galaxies in such a group is 1-3 million light years. The group to which our Milky Way belongs has 40 galaxies. In addition to the groups in the intergalactic space there is a huge number of dwarf galaxies. As a rule, such formations are satellites of larger galaxies, such as our Milky Way, Triangle or Andromeda.
Until recently, the smallest galaxy in the Universe was considered the dwarf galaxy "Segue 2", located 35 kiloparsecs from our star. However, in 2018, Japanese astrophysicists discovered an even smaller galaxy, Virgo I, which is a satellite of the Milky Way and is located at a distance of 280 thousand light years from Earth. However, scientists believe that this is not the limit. High probability that there are galaxies much more modest size.
For clusters of galaxies go clusters, areas of outer space in which there are up to hundreds of galaxies of various types, shapes and sizes. The accumulations are of colossal size. As a rule, the diameter of such a universe is several megaparsecs.
A distinctive feature of the structure of the universe is its weak variability. Despite the tremendous speeds with which galaxies move in the Universe, they all remain in one cluster. Here, the principle of maintaining the position of particles in space, which is affected by dark matter, formed as a result of a big explosion. It is assumed that, under the influence of these voids, filled with dark matter, clusters and groups of galaxies continue to move in the same direction for billions of years, adjacent to each other.
The largest formations in the Universe are galactic superclusters that unite groups of galaxies. The most famous supercluster is the Great Wall of the Clown, an object of universal scale stretching 500 million light years in length. The thickness of this supercluster is 15 million light years.
Under current conditions, spacecraft and technology do not allow us to consider the Universe to its full depth. We can only detect superclusters, clusters and groups. In addition, our cosmos has gigantic voids, bubbles of dark matter.
Steps to explore the universe
The modern map of the universe allows us not only to determine our location in space. Today, thanks to the presence of powerful radio telescopes and the technical capabilities of the Hubble telescope, man has managed not only approximately to estimate the number of galaxies in the Universe, but also to determine their types and varieties. Back in 1845, the British astronomer William Parsons, using a telescope to investigate clouds of gas, was able to identify the spiral nature of the structure of galactic objects, focusing on the fact that in different areas the brightness of star clusters may be more or less.
A hundred years ago, the Milky Way was considered to be the only known galaxy, although the presence of other intergalactic objects was proved mathematically. Our space yard got its name in ancient times. The ancient astronomers, looking at the myriad stars in the night sky, noticed a characteristic feature of their location. The main cluster of stars was concentrated along an imaginary line, resembling a path of splashed milk. The Milky Way Galaxy, the celestial bodies of another well-known Andromeda Galaxy are the very first universe objects from which the study of outer space began.

Our Milky Way has a complete set of all galactic objects that a normal galaxy should have. Here there are clusters and groups of stars, the total number of which is approximately 250-400 billion. There are clouds of gas in our galaxy, forming arms, there are black holes and solar systems like ours.
At the same time, the Milky Way, like Andromeda with the Triangle, is only a small part of the Universe, which is a part of the local supercluster group called Virgo. Our galaxy has a spiral shape, where most of the star clusters, clouds of gas and other space objects move around the center. The diameter of the outer helix is 100 thousand light years. The Milky Way - by the standards of space is not a big galaxy, whose mass is 4.8x1011 Mʘ. In one of the arms of Orion Cygnus is our sun. The distance from our star to the center of the Milky Way is 26,000 ± 1,400 sv. years old.

For a long time it was believed that one of the most popular astronomers among the Andromeda nebula is part of our galaxy. Subsequent studies of this part of the cosmos gave irrefutable evidence that Andromeda is an independent galaxy, and much larger than the Milky Way. The images obtained using telescopes showed that Andromeda has its own core. There are also clusters of stars, and there are nebulae that move in a spiral. Each time, astronomers tried to look deeper and deeper inside the universe, exploring vast areas of outer space. The number of stars in this universe giant is estimated at 1 trillion.
Through the efforts of Edwin Hubble was able to establish an approximate distance to Andromeda, which could not be part of our galaxy. This was the first galaxy to undergo such close scrutiny. The following years gave new discoveries in the field of intergalactic research. The part of the Milky Way galaxy in which our solar system is located has been studied more thoroughly. From the middle of the 20th century, it became clear that in addition to our Milky Way and the well-known Andromeda, in space there are a huge number of other entities of a universal scale. However, for the order required to streamline outer space. If stars, planets and other space objects succumbed to classification, then with galaxies it was more complicated. The enormous dimensions of the studied areas of outer space, which were not only difficult to study visually, but also evaluate at the level of human nature, had an effect.

Types of galaxies in accordance with the accepted classification
Hubble was the first to take such a step, making in 1962 an attempt to classify the galaxies known at that time in a logical way. The classification was carried out on the basis of the shape of the objects under study. As a result, Hubble managed to arrange all the galaxies into four groups:
- spiral galaxies are the most common type;
- elliptical spiral galaxies follow;
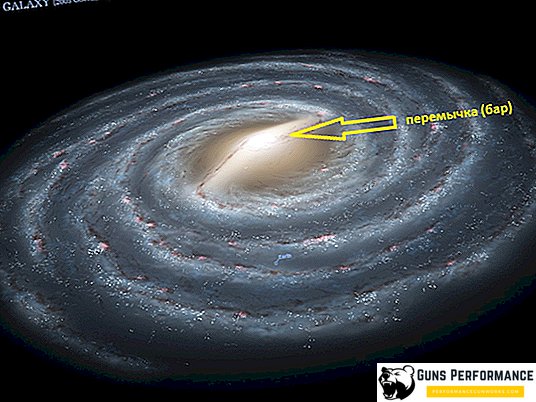
- with a jumper (bar) of the galaxy;
- wrong galaxies.
It should be noted that our Milky Way belongs to typical spiral galaxies, however there is one "but". Recently, the presence of a jumper - bar, which is present in the central part of the formation. In other words, our galaxy does not originate from the galactic nucleus, but flows from the jumper.
Traditionally, the spiral galaxy looks in the form of a spiral-shaped flat disk, in which a bright center is necessarily present - the core of the galaxy. Such galaxies are the most common in the Universe and are denoted by the Latin letter S. In addition, there are division of spiral galaxies into four subgroups - So, Sa, Sb and Sc. Small letters indicate the presence of a bright nucleus, the absence of sleeves, or vice versa, the presence of dense sleeves covering the central part of the galaxy. In such sleeves are clusters of stars, a group of stars, which include our solar system, other space objects.

The main feature of this type is slow rotation around the center. The Milky Way makes a complete revolution around its center for 250 million years. Spirals located closer to the center consist mainly of clusters of old stars. The center of our galaxy is a black hole around which all the main movement takes place. The length of the path according to modern estimates is in the direction of the center of 1.5-25 thousand light years. In the course of its existence, spiral galaxies can merge with other smaller universe formations. Evidence of such collisions in earlier periods is the presence of halo of stars and halo of clusters. A similar theory underlies the theory of the formation of spiral galaxies, which were the result of a collision between two galaxies located in the neighborhood. The collision could not pass without a trace, giving a general rotational impulse to a new formation. Next to the spiral galaxy is a dwarf galaxy, one, two or several, which are satellites of a larger formation.
Similar in structure and composition to spiral galaxies are elliptical spiral galaxies. These are huge, largest universe objects, including a large number of superclusters, clusters and groups of stars. In the largest galaxies, the number of stars exceeds tens of trillions. The main difference between such formations is a form that is highly stretched in space. The spirals are arranged in the shape of an ellipse. Elliptical spiral galaxy M87 is one of the largest in the universe.

With the jumper galaxies are much less common. They account for about half of all spiral galaxies. In contrast to spiral formations, in such galaxies, the beginning is taken from a jumper, called a bar, resulting from the two brightest stars located in the center. A striking example of such education is our Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy. Previously, this formation was attributed to irregular galaxies. The jumper is currently one of the main areas of research in modern astrophysics. According to one version, a nearby black hole sucks and absorbs gas from nearby stars.
The most beautiful galaxies in the universe belong to the type of spiral and irregular galaxies. One of the most beautiful is the Whirlpool galaxy, located in the celestial constellation Hounds Dogs. In this case, the center of the galaxy and the spirals rotating in the same direction are clearly visible. Irregular galaxies are chaotically located superclusters of stars that do not have a clear structure. A prime example of such a formation is a galaxy numbered NGC 4038, located in the constellation Raven. Here, along with huge gas clouds and nebulae, one can see a complete lack of order in the arrangement of space objects.

findings
You can explore the universe endlessly. Every time, with the advent of new technical means, a person opens the veil of space. Galaxies are the most incomprehensible to the human mind objects in outer space, both from a psychological point of view, and looking back at science.