To improve the flight characteristics of the MiG-21 fighter model, the Mikoyan Design Bureau, in the early 1960s, the development of a new flying machine began, a characteristic feature of which was to be a wing that could change its geometry. The first flight of a prototype - May 1967, the first serial flight - May 1969. In the Soviet Air Force in the mid-1980s, the MiG-23 was the most popular multi-role fighter and mass-produced.

Design features
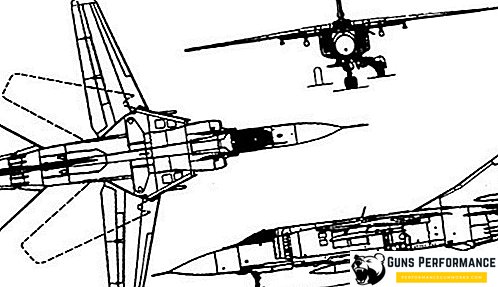
The design of the MiG-23 is a highly advanced aerodynamics with a variable geometry wing (sweep) and a full-circle tail stabilizer. The wing of the aircraft became mobile. The pilot, depending on the flight modes, could make it perfectly straight or swept, while removing part of the wing in the fuselage.
The wing itself is composed of two fixed parts fixed to the fuselage and two trapezoidal swivel cantilevers. Changing the sweep angle of the rotary consoles is possible within 16-72 °. The rotary wing assembly and the mount assembly of the movable console are made of two steel forgings and welded along the axis of symmetry as a decompressed welded structure.

MiGs could be equipped with wings of three different modifications. The wing of the first type was equipped with wheel arches and had a smoothed front edge. The following modification did not have a wing flap and was made with an enlarged chord in such a way that a “tooth” appeared on the front edge of the wing, due to which the sweep could increase by 2 ° 40 '. A special deflectable sock and a “tooth” were added to the drawings of the third type of wing. Wings of all types had two-piece spoilers and three- or four-section flaps.
The fuselage has a semi-monocoque design and is divided by a technological connector into the tail and nose parts. The nose compartment with the onboard radio-electronic equipment and the cabin of the pilot are sealed. On the detachable rear fuselage are four air brakes.

The cockpit is equipped with a lantern and a viewing device for the rear view of the TC-27AMSH.
The aircraft has an afterburner turbojet engine R-35-300 with a thrust of 13,000 kg. Its design and drawings for it were developed at the AMNTK Soyuz (ch. Konstr. Khachaturov). Its main technical characteristics:
- maximum speeds (near the ground - 1350 km / h, at an altitude of 2500 km / h);
- rate of climb - 12,900 m / min;
- range with three full suspension tanks - 2360 km.
The air intakes of such a power plant are made lateral and are regulated with the help of movable wedge flaps. The engine can withstand the attacks of the ZRK missiles and the warheads of air-to-air guided missiles.

The chassis is made of three bearings, with the front pillar (nose support) specially reinforced and has two wheels CT-152 with an increased diameter (520 x 125 mm), and the main supports were specially extended by 175 mm and each equipped with one wheel CT-150E with dimensions 840 x 290 mm. Disc brakes with pneumatic drive, wheel pneumatic - tubeless.
Armament of the MiG-23 fighter
Gun-rifle armament is represented by a built-in 23-mm double-barreled gun GSH-23L with ammunition - 260 rounds.

Radar RP-21 makes it possible to use guided weapons of the class "air-to-air" and "air-to-surface":
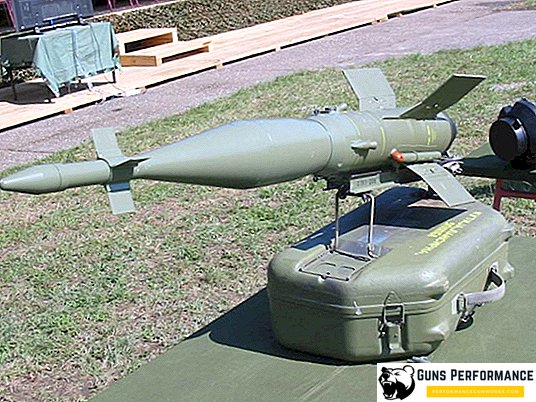
- medium-range missiles R-23R and R-24R with a radar guidance system;
- R-23T and R-24T with TGS;
- short-range missiles R-60 and R-60M.
For destruction of ground targets using air-to-surface weapons. It may be:
- guided missile with guidance on the beam X-23;
- bombs weighing up to 2000 kg;
- HAR-gun containers and HAR-blocks.
The use of the Mig-23 in hostilities
The MiG-23 and its various modifications were exported to the Air Force of such countries as Angola, Algeria, Cuba, Bulgaria, Libya, Egypt, Germany, Iraq, Syria, India, Vietnam.
The first major military confrontation, where the MiG-23 was used, was the aerial battle in June 1982 between Israeli and Syrian aircraft. Not only the Syrian, but also the Israeli pilots noted the impressive accelerating characteristics of the fighter, ease of control of the onboard equipment, precise controllability at high angles of attack.
This model of fighter since 1979 has been widely used during the conflict in Afghanistan. Parts of the Soviet Air Force equipped with MiG-23 aircraft, were based on the airfields of Bagram and Kabul and solved defensive tasks with possible actions by the Pakistan Air Force. Sufficiently successful combat use of the MiG-23 in high-altitude conditions, provided the unique take-off and landing characteristics of this aircraft.

Mig-23 fighters belonging to Iraq were actively used during the period of armed conflict between Iran and Iraq from 1980 to 1988. Aircraft performed the task of intercepting Iranian aircraft F-14A (Tomkat) and F-4, as well as for the application of rocket and bombing attacks on ground targets.
Another of the territories where there was combat use of the Mig-23 was Angola. In 1985, 50 Mig-23s were sent there, piloted from Cuba. Their rivals in the air were Mirage F1 and Mirage III of the Republic of South Africa. The Angolan Air Force scored several air victories, showing serious air superiority over the enemy.












