On April 5, 2016, the citizens of Russia were surprised to learn that soon another country’s federal security structure would appear in the country - the National Guard. It was on that day that the relevant decree of President Putin was signed, and bills regulating the activities of the new structure were sent to the State Duma. The number of new departments can reach 400 thousand people.

This decision was like thunder in a cloudless sky, it was so unexpected that it caused bewilderment among experts and the public. Even more questions are caused by the possibilities and powers of the new service, which can be called unprecedented. According to the presidential decree, the National Guard of the Russian Federation will perform a number of functions within the country, and it will personally obey Putin. The command of the new power structure will be one of the most loyal people to the president - Army General Zolotov.
Ideas about the creation of the Russian National Guard were voiced in the early 90s of the last century. Later, we returned to the discussion more than once, but it didn’t go further. And suddenly, without any information campaign, without public discussion, even without rumors and injections, a decision is made that completely reformats the power bloc of the state.

Structures like the Russian National Guard are a product of periods of political instability, unrest and revolutionary hard times. It would be much more logical for the National Guard to appear in the 90s, in times of chronic lack of money, separatism, social protests and the Caucasian wars. Why was it needed today, when Putin’s ratings are exorbitant, and his political opponents are demoralized and are not capable of anything serious?
Opponents of the current Russian regime have already managed to christen the newly created structure of the new oprichnina, drawing parallels with the epoch of Ivan the Terrible, after which Russia fell for a long time in the Time of Troubles.

A little about the history of the National Guard under
The word "Guard" of Italian origin, it translates as "guard, guard". Guard called military units, staffed by the best, selective fighters. As a rule, the guard was not part of the army. At different times and in different nations, the functions of the guardsmen differed. They were often entrusted with the task of guarding the first person of the state (Praetorian guards in Rome) from conspiracies and assassinations. Often the guard carried out police functions, participated in the suppression of insurgency and uprisings.
The term "national guard" appeared at the end of the XVIII century in revolutionary France, together with the appearance of the first national state. The French Guardsmen were ideological supporters of the revolution and were engaged in suppressing speeches and revolts against the new government, ensuring public order on the streets. Often performed punitive functions. It was the National Guard that participated in the bloody suppression of the Vendeo insurgency. It should be noted that the French National Guard did not differ special reliability, it supported one or the other political force. In the end, the French dispersed these troubled troops.
Today, many states have paramilitary units called the National Guard, or structures with different names, but performing approximately the same tasks. Such troops can be divided into two types: "European" and "American". The main task of the European national guard is the protection of the constitutional order and public order. In fact, it is well known to us internal troops.

The main task of the American National Guard is to work with a mobilization reserve in case of a major war and general mobilization. At the same time, American guardsmen are also involved in disaster relief (Hurricane Katrina), and resist large-scale street riots.
The US National Guard is staffed only by volunteers, they serve in parallel to the main work. For this, the guardsmen have a lot of bonuses and benefits from the government. The US National Guard took part in the hostilities in Iraq and Afghanistan, although reviews of their effectiveness and professionalism on the battlefield are highly controversial.
The United States National Guard has dual subordination: to the federal and state governments. For the federal center, the guards are the primary military reserve that will be involved in mobilization.
In most of the CIS countries (and earlier in the USSR), the internal troops, recruited on conscription basis, deal with the protection of the constitutional system and order on the streets.

Separately, it should be said about the militarized structures that bore the name "National Guard", but at the same time performed very specific tasks. As an example, some of the paramilitary forces of Latin and South America can be cited.
The National Guard under Nicaragua consisted of professional mercenaries and participated in the civil war that went on for many years in this country. In fact, it served as the army and led a long-term anti-guerrilla war.
The National Guard of El Salvador also took an active part in the troubled political life of this Latin American country. She participated in numerous coups and revolutions, fought with partisans, persecuted citizens for political reasons. It was in the National Guard that the famous "death squads" were organized, which abducted and killed the representatives of the left movements.
There is also a national guard in Venezuela. In addition to the dispersal of demonstrations, the Guardsmen have recently been attracted to perform more specific tasks: they are struggling with shortages and rising prices. For this, the troops occupy the shops and take the factory by storm.
The main task of the National Guard of Saudi Arabia is to protect the monarch and members of the royal family. In Azerbaijan and Kyrgyzstan, the main function of national guardsmen is to protect the institutions and top officials of the country.
The National Guard of Ukraine appeared in 1991, but then this structure was abolished. The second birth of the Ukrainian guard occurred in 2014. Today, it includes both former units of the internal troops performing purely guard functions and voluntary battalions taking part in hostilities in the Donbas.
SS and IRGC as the progenitors of the Russian Guard
Separately, it is worth mentioning two military units, one of which exists today, and the second was recognized as criminal during the Nuremberg Tribunal - the Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC) and SS guard detachments created back in Nazi Germany.
The IRGC is an elite military unit created immediately after the 1979 revolution. Officially, this structure is part of the armed forces of Iran, but in fact has its own commander in chief and reports directly to Ayatollah Ali Khamenei.

The corps has its own armed forces, which include ground forces, aviation, naval forces and special operations units capable of operating outside the country.
The IRGC took an active part in the Iraq war, and now the Corps units are fighting on the side of Bashar Assad against insurgents in the Syrian conflict. The soldiers of the IRGC are considered to be among the most efficient in the Iranian army.
In addition to participating in hostilities, the Corps is engaged in ensuring internal security, fighting "against subversive elements" inside the country, and promoting the ideas of Islam outside of Iran. Corps fighters maintain public order and protect important government facilities.
The corps is engaged in the preparation of the Basij militia, a militarized structure that performs many functions. The number of this formation is 10 million people.
The leadership of the IRGC pays great attention to the ideological training of its fighters, as well as the dissemination of their ideas among the population of the country. The corps owns the media (TV channels, newspapers, radio stations).

SS guard detachments appeared in Germany in 1933. Initially, they were created to protect the members of the Nazi party and its Fuhrer Adolf Hitler.
In 1940, SS troops (Waffen-SS) appeared, reporting directly to Heinrich Himmler. SS units were only part of the German army, but in reality it was a Nazi party paramilitary force.
Also, the SS consisted of units that ensure the protection of concentration camps and participated in the mass extermination of people.
The SS controlled practically all the operational, search and intelligence activities of the Third Reich through the Security Service (SD) and the General Directorate of Imperial Security (RSHA).
In addition, the SS carried the protection of the entire senior management of Hitler's Germany, was engaged in scientific projects and ideology. Gradually, from the security structure of the SS turned into the main personnel reserve of Hitler's Germany.

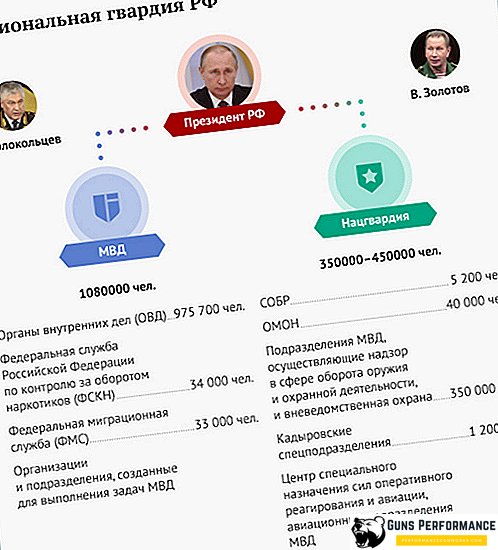
Rosgvardiya - the national guard of Russia
The Russian National Guard is formed on the basis of the current internal troops, as well as special units of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, such as SOBR, OMON, CPSSOR. The National Guard will also include a private security department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
The main functions of the Russian National Guard under:
- protection of public order;
- the fight against terrorism, extremism and organized crime;
- control of weapons circulation in the country;
- protection of public facilities and cargo;
- providing security services to individuals and legal entities, as well as monitoring the security services market.
The National Guard of the Russian Federation is assigned to special services. The acquisition of this structure is mixed: both by contract and by conscription.
The national guard has the right to detain, infiltrate homes and conduct searches.

If we talk about what the Russian National Guard still looks like, then more than other options it resembles the police units of Latin America. Without a doubt, the functions of the National Guard, prescribed in the presidential decree, exceed the capabilities of the classical internal troops.
There is a certain similarity between the Russian National Guard under the Iranian IRGC and the Nazi SS, but there are significant differences. The most important of them is that the two foreign structures mentioned above were (and are) primarily the bearers of a certain ideology.
The SS was not only a militarized organization, it actively supplied its cadres to the state apparatus of Hitler's Germany and thanks to this, it managed the country in the interests of the Nazi party.
The Iranian Guard Corps also cannot be called a structure that performs purely security or military functions, it is the carrier of the ideology of the Iranian revolution and has a strong influence on the life of the state.
It is still not completely clear what the Russian National Guard will look like. It is not clear whether she will receive the right to engage in operational investigative activities, but something suggests that such a right will be granted to her (albeit not immediately).
We will venture to suggest that this will be the president’s personal army, with the help of which the head of state hopes to ensure the loyalty of the Russian elites.

What created the national guard of Russia
Why did the authorities initiate the creation of the National Guard now? There are several hypotheses.
According to the first of them, Putin is so scared of the possibility of implementing the scenario of the color revolution in Russia, that he decided to play on the lead and create a structure that can suppress any riot. Indeed, the standard of living in the country is falling, this applies to both the capital and the regions. The experience of the protests on Bolotnaya Square in early 2012 showed that the protest potential in Russia exists. True, many things have changed since those events, but the hypothetical danger has remained.
Today, the authorities have several tens of thousands of SOBR and riot policemen, and this may not be enough even to quell serious unrest in the capital. In 2012, they had to be urgently brought to Moscow by various means of transport.

For the inspection and detention of the guards will not need the approval of the prosecutor or a court decision. Only then can they inform the prosecutor "at the discretion of their supervisor." It is not known whether such a rule will remain in the draft law, but not a single Russian federal power agency has such powers.
However, this hypothesis causes skepticism. Despite the economic turmoil, the growth of protest activity in Russia is not observed. Society is split, stunned by propaganda, has no leaders. In such a situation, with any unrest you can easily cope with the power tools available.
Some of the experts express the idea that Putin is creating a personal army (about 400 thousand people), in order to guarantee the avoidance of a palace coup.
The events of recent years, Western sanctions, the policy of self-isolation can not but cause irritation of a part of the Russian elite. And any color revolution always begins with a split in the elites, and the Ukrainian Maidan is a clear confirmation of this.
Whether such a militarized structure will be effective in this case is a moot point. As historical experience shows, the guards often stand aside during the insurrection or take part in it. The guards did not lift a finger to save the last Russian emperor Nicholas II.
After the creation of the National Guard, the units of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (SOBR, OMON) will be less dependent on regional authorities and become more controlled for the federal center.

Another interesting theory, which explains the need to create a national guard, was put forward by the journalists of Novaya Gazeta. In their opinion, the National Guard is, first of all, a blow to the head of the Chechen Republic, Ramzan Kadyrov. Say, in this way, the federal center is trying to knock out its main trump card from the hands of the willful regional leader - the militarized structures that are nominally part of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, but are personally subordinate to Kadyrov.
According to Russian journalists, after the Chechen battalions join the National Guard, they will no longer be so committed to the Chechen leader, but will be controlled by the federal center. Such a theory sounds rather naive: the Chechen divisions are still part of the Russian power structures, but in fact they are subject only to Kadyrov. The East, as is known, is a delicate matter. And the Caucasus is no exception.

Formally, the Chechen units may be subordinate to the new commander in chief, but in fact everything will remain the same. In addition, Zolotov has excellent personal relations with Ramzan Akhmatovich (unlike many other federal security forces), so interaction issues are likely to be decided on a personal level.
The current transformation, which began with a presidential decree, could seriously disrupt the well-established balance between Russian law enforcement agencies. The Ministry of Internal Affairs will suffer the most, which will lose part of the structures and significant financial flows.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs is deprived of special units (Special Forces and Special Forces, Special Police Force (OMBR), special militia forces), they are deprived of private security, control over the circulation of weapons. This is a serious blow. True, the FDCS and the FMS will now be part of the Ministry of Internal Affairs - but this is an unequal replacement.
In addition, the lack of rapid reaction units and riot police can seriously complicate the work of the police, the fighters of these units are often attracted to the detention of criminals or other operations. If they are subordinate to another department, it will seriously complicate the lives of the police.
While it is still early to assess the new power structure. It takes several years to carry out such a reform.













