The history of world tank building knows quite a few cases when the created equipment, according to its tactical and technical parameters and characteristics, hardly fit into the military concept existing at the time. A similar situation arose with the appearance on the battlefield of the steel monster, the Soviet heavy tank KV-2. Despite the fact that weapons of this format could not find their real place on the battlefield, the appearance of such a tank was a landmark event not only for the USSR armed forces, but also for world tank design. This was facilitated by a number of factors, both strategic and political. Soviet heavy tanks, created before the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, their appearance gave a powerful impetus to the subsequent development of this kind of troops. Steel hulk, invulnerable to artillery fire, contributed to the emergence of new tactics in the existing concept of the use of tanks.
The history of the creation of the KV-2 tank
The reasons that prompted the Soviet designers to create such an unusual tank, lie on the surface. In the late 30s, the armored forces of the Red Army were perhaps the most numerous in the world. The main park of the Red Army was represented by models of light tanks T-26 and a series of BT. Maneuverable and light vehicles were the main striking force able to quickly solve operational and tactical tasks in open areas. For its time, these were quite successful cars. The only drawback of Soviet tanks was weak armor protection.

The anti-bullet reservation could not provide the Soviet T-26 and BT with reliable protection against enemy artillery fire. The military operations on the Karelian Isthmus during the Winter War of 1939-1940 clearly demonstrated the vulnerability of Soviet armored vehicles to artillery fire by the defending Finns. In addition, the Soviet troops had to face the overcoming of deep-echeloned defense, which was based on the long-term fortifications of the Mannerheim Line. Light and maneuverable tanks, armed with 45 mm cannons, with weak armor, became useless for conducting offensive operations in the conditions of the enemy's strong and long-term defense. Finnish bunkers and bunkers, armed with machine guns and artillery, quietly shot the attacking infantry, easily destroyed Soviet tanks in the assumption of defensive positions. The shelling of the fortifications of Finns by the Soviet large-caliber artillery and airstrikes did not give the desired effect.

Attempts to use the T-28 tank and the heavy, five-turreted T-35 to be armed with long-term fortifications were not crowned with success. Weak artillery heavy machines did not have the technical capabilities for the destruction of concrete protective structures. Even the heavy KV-1 tank that appeared on the Finnish front in the winter of 1940 could not fully solve the tactical tasks assigned.
It required an effective means of destruction for close combat, capable of destroying long-term firing points with point-blank shots. A technique was needed that could deliver a heavy large-caliber gun to the front, from which it was possible to fire direct fire. Self-propelled artillery at that time was in an embryonic state, the main emphasis was placed on heavy tanks. The heavy assault tank KV-2, which appeared in the North-Western Front in January 1940, became an effective way out of the current situation. This giant with a disproportionately large turret possessed not only tremendous firepower, but also was invulnerable to enemy artillery fire.

The new tank was able to get close to enemy long-term firing points, shooting them from a powerful 152 mm gun. From a distance of 200-400 meters, Soviet concrete and high-explosive shells of this caliber turned concrete fortifications into a pile of debris. The tank itself remained virtually unscathed. The only weapon that could stop the steel community was the Finnish anti-tank mines.
Description of the design of a heavy tank KV-2
The new tank continued the series of Soviet heavy tanks KV (abbreviation KV - Kliment Voroshilov) of the new generation. The first machine of this type, the KV-1, had powerful armor and was armed with a 76 mm gun. The tank was designed to break through enemy defenses in the field. Rather high tactical and technical characteristics of the new machine allowed it to successfully operate on the battlefield in suitable conditions. A striking example of the high efficiency of the Soviet heavy tank technology is the fact that the Soviet first KV passed the test of fire not only during the Winter War, but also continued to be used by the Red Army throughout the initial period of World War II.
It was on the basis of the first KV that Soviet designers decided to create a more powerful machine capable of successfully fighting the enemy’s long-term fortifications. At Kirov tank factory, under the leadership of J. Y. Kotin, a draft of a tank armed with a howitzer was developed for two weeks. During the development of the project, it was necessary to radically change the concept of the tank design. Inside the tank tower of the KV-2 tank, it was necessary to place not only a powerful gun, but also to provide space for a full-fledged artillery crew.

The first sample under the U-1 index entered the military range already in January 1940. A review of the new car should not begin with the chassis, which is mainly preserved from the previous car, but from its tower. There was no such thing in the history of world tank building. On the tank chassis, the designers decided to install a 152 mm howitzer M-10 in a tank version, with a shortened barrel. The new gun received the index m-10T. The installation of such a powerful gun for the tank required the creation of a new large tower. The use of a tank as an artillery platform did not put any restrictions on Soviet designers to achieve stealth on the battlefield. During the development, two versions of the MT-1 and MT-2 towers were used. After conducting fire tests, military experts and designers stopped at the second option, in which the tower had a smaller area of destruction.
The main concerns of the developers of the new machine, related to the impact of the enormous recoil force arising from howitzer firing, on the position of the machine, did not materialize. The tank after the shots continued to maintain stability. The hull of the tank was sheathed with armor 30, 40, 65 and 75 mm thick on the sides and in the frontal part. Separately, it is worth staying on booking a tank tower. For these purposes, armored plates 75 mm thick were used. The gun mask had a thickness of 110 mm. Such a powerful reservation at the time did not have any model of the tank in the world. Existing at that time, samples of tank and anti-tank guns were powerless to penetrate such thick armor, firing from any distance. The tower was equipped in the aft door, facilitating the actions of the crew in combat conditions.

For such a large tower, it was necessary to increase the shoulder strap to 1535 mm. The tower, mounted on the fighting compartment, was fixed with special clamps, ensuring its stability during firing and with a strong roll of the machine. The KV-2 tank turret had angles of rotation designed for direct fire and closed firing positions. Inside the tower there was enough space for the combat crew of an artillery gun consisting of 4 people. In the fighting compartment housed seats mechanic - the driver and gunner radio operator. The landing and evacuation of the crew of the vehicle was provided through the hatch and the aft door, located in the turret, through the hatch in the fighting compartment. In the bottom of the tank there was also an emergency inlet / exit hatch. Access to many units and aggregates of the tank was provided through the bottom of the tank, in which for these purposes there were special technological holes.
After the tests, experiencing an urgent need for such a technique, the Government decided to launch the machine into mass production as a matter of urgency.
Combat use of the KV-2 tank
A review of the combat use of the new machine should begin with its actions on the battlefield during the Soviet-Finnish war. The tank was specially created to overcome the fortifications of the Mannerheim Line. As it turned out, the new heavy assault tank successfully coped with the task. Despite the fact that at the time of the appearance of a heavy steel monster on the Karelian Isthmus, the Finnish army was drained of blood, the effect of the new machine showed the correctness of the decision.

Acting in the zone of the advancing troops, the Soviet KV-2 could quickly suppress the enemy’s long-term gun emplacements, shooting concrete fortifications with concrete shells and hitting the enemy’s infantry with their machine guns. The tank, adopted by the Red Army in February 1940, was mass-produced only at the Kirov tank factory in Leningrad. Until July 1941, more than two hundred heavy vehicles were produced, which were part of the tank units of the Baltic and Western military districts. Already during the first months of the German offensive, almost all Soviet super tanks were lost.
The reasons for such large losses are not in the weakness of the design of the Soviet heavy tank, but in the absence of the necessary technical and combat conditions for the effective operation of weapons of this type. The Red Army in the first months of the Great Patriotic War had to fight defensive battles. The need for assault tanks for use on the battlefield, as such, was absent. Soviet tank crews had to conduct tank battles in full or partial environment. In direct collision with the German tank units, the Soviet KV-2 was certainly an unsurpassed weapon. German medium tanks PzKpfw-III PzKpfw-IV could not hit the Soviet leviathan with their guns. German tank units won battles due to the best control system on the battlefield and thanks to the maneuverability of their vehicles.

None of the anti-tank guns of the German army in the initial period of the war could not penetrate the 75 mm KV-2 armor. However, even in the absence of an equal opponent on the battlefield, Soviet heavy tanks suffered huge losses. Affected by the lack of proper control of tank units in the troops. Often the lack of ammunition, spare parts and fuel led to the fact that the crews were forced to leave their cars on the battlefield. Most of the Soviet heavy tanks in the first months of the war were lost for technical reasons. Only a small part, no more than a third of the total available number of KV-2 tanks in the army, was destroyed as a result of the actions of German assault aircraft and from heavy artillery fire.
Technical characteristics of the KV-2 1940 model tank
- Years of production: 1940-1941.
- Total manufactured: 204-304 pcs.
- Combat use: World War II.
- Crew - 6 people.
- Combat weight: 52-54 tons.
- Length - 6.67 m, width - 3.32 m, height - 3.24 m, ground clearance - 430 mm.
- Armament: 152-mm howitzer cannon (loading separately-cartridge, ammunition - 36 shots).
- The main types of ammunition: armor-piercing and concrete-piercing shells, high-explosive steel howitzer grenade.
- Armor thickness: body front - 75 mm, side - 75 mm, tower - 75 mm.
- Diesel engine, power - 600 hp
- Maximum speed on the highway - 35 km / h.
- Cruising on the highway - 225 km.
- Overcoming obstacles: wall - 0.87 m, ditch - 2.7 m.
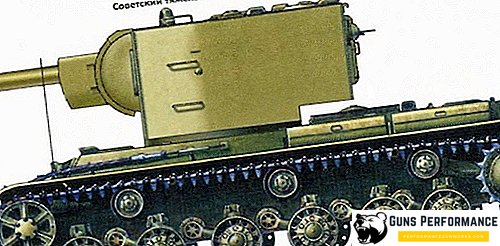
Tank photo