One of the main paradigms of Western civilization these days is the recognition of human life as the highest value. But such humanistic ideas come into conflict with the need to fight and train servicemen for them. The death of their own soldiers is not only not consistent with abstract values, but is also very poorly perceived by voters, to whose opinion modern politicians listen sensitively.

Modern Western armies are doing everything possible to reduce the number of losses. The fighters are provided with the most modern equipment, communications, body armor. The United States and its allies conduct ground operations only in extreme cases, trying to confine themselves to rocket or bomb strikes from the air. However, most often it is impossible to win a war without a ground operation.
The most promising solution to this issue is to replace soldiers on the battlefield with robots. Active developments in this direction are carried out in many countries, but the USA is still the leader. Already today, automated combat systems are widely used in Afghanistan and Iraq. The lethal weapon is not trusted so much by them, but the robots have already very successfully neutralized mines, carried out reconnaissance and observation.
In 2007, robots participated in a real battle in Iraq for the first time. The test was not very successful, but the US military does not abandon the idea of calling "terminators" into their armed forces. Work in this direction is underway in Russia, but not as actively as in the West.
However, in general, it can be said that the use of automated systems on the battlefield is one of the most promising areas for the development of military affairs. We are still not too good at doing mechanical assistants, but many experts believe that in the next decade, humanity will expect a breakthrough in this area. Unfortunately, most likely, new technologies will be among the first to be used for war and destruction.
Types of modern military ground robots
Modern ground military robots can be divided into the following groups:
- reconnaissance;
- engineering;
- combat;
- rear.
It should be noted that for many automated devices, this separation is somewhat arbitrary. They are unified platforms on which, depending on the needs, certain modules are installed. So a sapper robot can be easily turned into a combat robot.

Actually military robots can be divided into three large groups:
- lungs;
- medium;
- heavy.
A military robot consists of a remote-controlled vehicle and a remote control from which it is controlled. Robotic mechanisms differ in their degree of autonomy, they can more or less follow the nested program and do without constant human intervention. Already today there are dozens of types of purely military robots, distinguished by their size, body shape, chassis, and the presence of various manipulators.
At the mention of military robots, the first thing that comes to mind is anthropomorphic terminator robots from science fiction films. They have their own intelligence and can act autonomously. However, while this picture is not true. Similar automated systems already exist (although artificial intelligence is not yet discussed), but their cost is enormous. Therefore, military robots today are automated or remotely controlled platforms.
In addition to the fact that modern android robots are very expensive, there are hardly any tasks on the battlefield that they would perform better than a professional soldier. The creation of a real robot soldier who would have intelligence to one degree or another is connected with solving a whole range of tasks in the field of cybernetics, control systems theory, the development of new materials and energy sources.
Intelligence robots
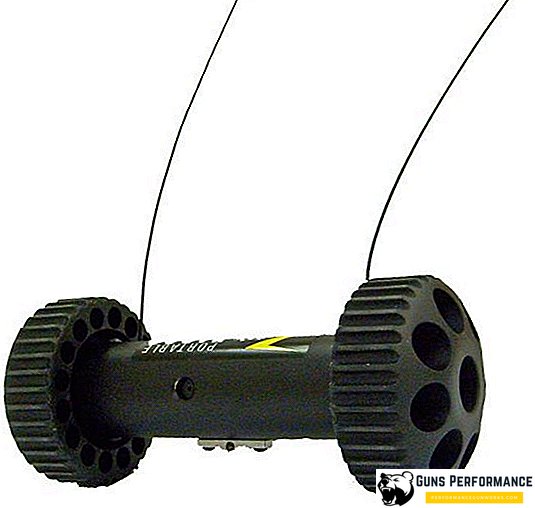

Automated systems have long been used to gather intelligence, search for targets and target designation, and monitor the situation. Both unmanned aerial vehicles and ground robots are used for such purposes. One of the smallest reconnaissance robots used today by the US Army in Afghanistan is the Recon Scout. It has a weight of 1.3 kg and a length of 200 mm, equipped with a conventional and infrared camera. This robot can be thrown behind obstacles, but it can only move on a relatively flat surface.

Another representative of the group of reconnaissance robots is First Look 110. It weighs 2.5 kg, has tracks and is controlled from a console located at the operator on the wrist. The robot is equipped with four cameras and can overcome small obstacles. Other sensors can be installed on it: thermal imagers, indicators of biological, chemical and radiation contamination.

Another remotely controlled vehicle actively used in the US Army for reconnaissance missions is Dragon Runner. This robot is also equipped with a tracked chassis, it is designed for the front line of fighting. Dragon Runner is carried in the knapsack, you can throw it through any obstacles.

The most massive American military robot (released more than 3 thousand pieces) is TALON, developed by Foster-Miller. This car is very fond of American soldiers, it was very effective in Afghanistan. This robot is perfect not only for reconnaissance, but also for disarming explosive devices. It was TALON who actively used for reconnaissance of caves, where the Taliban hid, on the account of this robot 50 thousand defused explosive devices. The US military even decided to give TALON weapons "to manipulators." A modification of the robot was created, on which it was possible to install a machine gun, sniper rifle or ATGW. It shoots a robot with a truly sniper accuracy.
By the way, the Americans noted an interesting phenomenon: the fighters are strongly attached to the robots, treat them as comrades or pets.
As we can see, the line between different groups of military robots is often quite thin: an automated system can conduct reconnaissance, and detect mines, and directly participate in hostilities.
Engineering robots
This is another extensive group of mechanisms that are usually remotely controlled. Engineering robots are used for the disposal of mines and land mines, creating passages in minefields, lifting weights and clearing debris.
An important trend in the development of such machines was an increase in their mass, which made it possible to attract remotely operated machines for more serious work. In the US, now all engineering machines are controlled remotely.

A typical example of such a technique is the engineering machine MV-4 (or M160). Its mass is 5.32 tons, it has a tracked chassis and is used for the disposal of ammunition and mines at a depth of up to 320 mm. You can control the MV-4 from a distance of two kilometers, which makes the work of sappers completely safe.

An even heavier engineering machine with a remote control is ABV (Assault Breacher Vehicle), which in its mass and armor protection is comparable to the American OBS Abrams. ABV is equipped with a mine trawl and demining charges, it can put smoke screens. Now in the United States are working on a fully autonomous modification of the machine.
There is a huge number of small sapper robots that are actively used not only by the military, but also by the police and special services. They have become familiar, and we often see them on TV. Indeed, why risk people if you can send to examine a suspicious object of a robot with a camera and a manipulator?
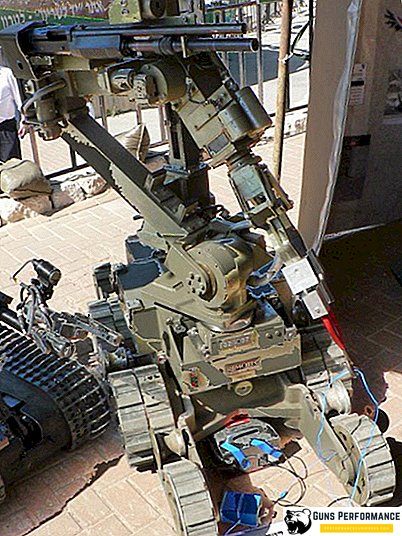

One of the most famous robots for mine clearance is MarkV-A1, created by the American company Northrop Grumman Corporation. It has several video cameras installed, as well as a water cannon to destroy bombs. Currently, the MarkV-A1 is used by special units of the United States, Israel and Canada.
Fighting robots
Of course, the greatest interest among the public cause combat robots. However, this group of ground-based automated machines is not yet very developed. Modern battle is very complicated, short-lived, and decisions need to be made instantly, quickly changing their position. All this in modern automated systems is still not very good. Anthropomorphic fighting robots are rather technical exotics that they work on in laboratories. Most combat robots today have a wheeled or tracked chassis, they are controlled via a cable or radio signal.

One of the most well-known combat autonomous systems is the Israeli Guardium unmanned vehicle, which is used for patrol service, guarding and escorting colones, as well as for conducting reconnaissance. The car is created on the chassis of the buggy, has good speed and throughput, you can install weapons on it. Guardium was adopted by the Israel Defense Forces in 2009.
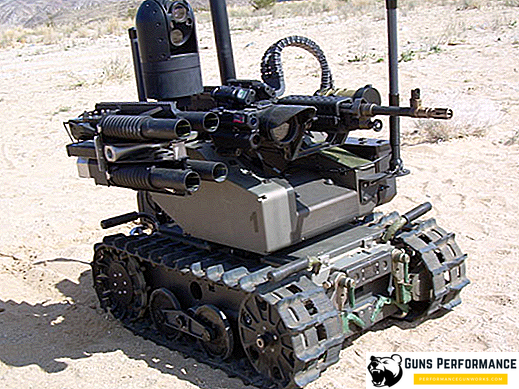
The most massive and highly recognizable combat robot is the already mentioned TALON, or rather, the SWORDS robot created on the basis of this platform, capable of carrying a sniper rifle, grenade launcher and machine gun. The cost of one unit is $ 230 thousand, but the manufacturer promises to reduce the price by almost half (to $ 150 thousand) after the start of mass production.
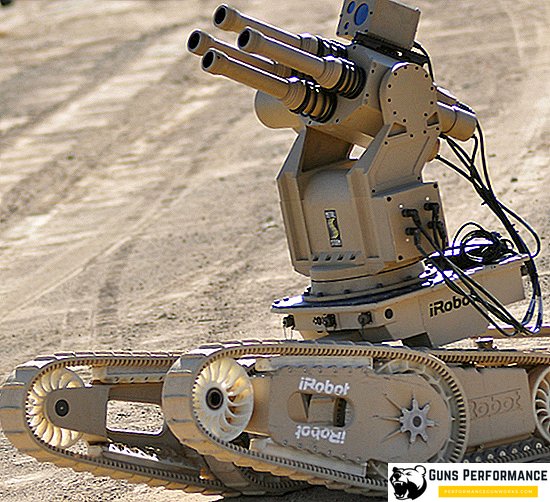

Another robot that can fire at the enemy is Warrior, created by the American company iRobot. You can install a 7.62 mm machine gun, an automatic shotgun, anti-tank systems and other weapons on it. Warrior can be used as a sapper, he can carry the wounded from the battlefield.

In 2010, Northrop Grumman introduced another development of its own - the CAMEL combat robot. The customer was the American Agency for Advanced Study DAPRA. This is a flat platform on a wheel track, which in addition to weapons can carry 550 kg of cargo. Rubber tracks can be worn on the wheels, which significantly increases cross-country CAMEL cross-country ability. The robot can accompany the combat units and move autonomously, guided by GPS signals.

Another promising American robot is the Crusher ("crush" or "destroyer"). This is a wheeled car weighing 6.5 tons. Its feature is a high cross and the ability to overcome significant obstacles. Crusher is equipped with several video cameras, a laser range finder, a thermal imager, you can install various types of weapons on it.
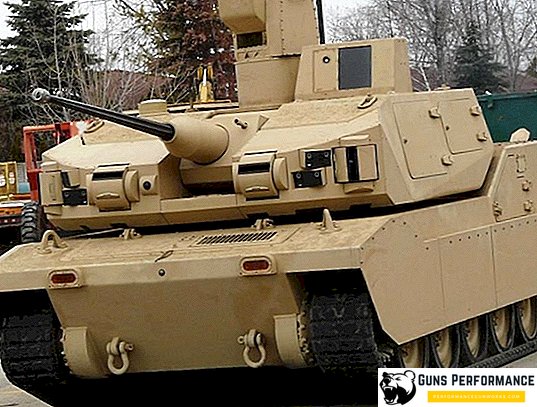

The largest combat robot today is Black Knight, developed by BAE Systems (USA). This tracked vehicle has a weight of 9.5 tons, armed with a 30-mm automatic cannon and a machine gun paired with it. The robot is equipped with television cameras, thermal imagers, radar, satellite navigation system. Black Knight controls are made from a special command vehicle or from Bradley BMP.
Rear robots

A separate group consists of robots intended for the transport of goods, including in the area of hostilities. Such systems must accompany the fighters and transport part of their ammunition, heavy weapons and other goods. Almost all such robots can perform additional functions: reconnaissance or evacuation of the wounded.

Examples of such machines are SMSS, R-Gator and TRAKKAR. Separately, it is worth mentioning the American robot porter BigDog, which moves on four limbs and can theoretically pass where the wheeled vehicle is not capable of moving. But this development is still experimental.
And what about us?
Russia has a good start in this direction, although there is some lag in communication and control systems. The centers of domestic robotics are OJSC "Izhevsk Radio Plant", MSTU. Bauman, NITI "Progress" (Izhevsk).

At the Izhevsk Radio Factory, a universal robotic platform IRA was created, which, depending on the configuration, can perform various functions. This robot is small, but it has a very impressive arsenal: two grenade launchers, two Bumblebee rocket-projectiles, a Pecheneg or Kord machine gun. MRK can be remotely controlled at a distance of 500 meters. The robot is equipped with a video camera, microphone, lighting system.
This complex was originally designed for parts of the Strategic Missile Forces to protect launchers of ICBMs.
Like most other modern combat robots, ISCs are a universal platform on which you can install additional equipment and weapons.
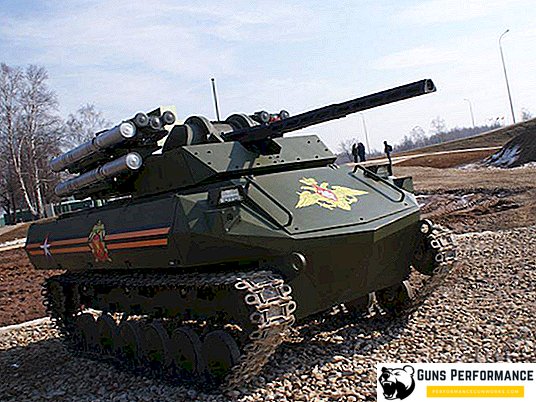

Another Russian automated combat system is Platforma-M. It was developed at the NITI Progress and was first shown to the public in 2018. The platform can be used for reconnaissance (there are video cameras, a thermal imager, a radar station, a range finder), patrolling the area, support for assault units. Platform-M can be armed with an automatic grenade launcher, machine gun, anti-tank systems. The weight of the machine is 800 kg, the payload is 300 kg. You can control the “Platform” at a distance of up to 5 km.
There is information that this machine is used by Russian troops in Syria.

The heaviest Russian robotic combat system is Uran. The weight of this machine reaches eight tons. On the basis of "Uranus" created fire support machine, mine trawl and fire engine. "Uranus" has repeatedly participated in various exercises.
In 2018, Rosoboronexport announced the start of the promotion of the Russian automated complex Uran-9 on the world arms market.
On the prospects of military robots
Robotics are paying special attention around the world. In the past few years alone, the Pentagon has allocated $ 4 billion to develop military robots. However, the civil sector still sets priorities in this direction. At present, it cannot yet be said that robotics strongly influences the sphere of defense and national security. However, things can change very quickly.
The development of automated systems is at the forefront of science and technology development. To create a truly effective combat robot, you need to solve many of the most complex technical problems. This is the development of fundamentally new energy sources, powerful and compact, and the creation of advanced sensors, and the provision of more reliable communications.
At present, the robots used by humans (including the military) resemble radio-controlled toys more than the mechanisms described by Asimov and other fiction masters.












