Since a significant part of Russia is occupied by various kinds of forests, steppes and swamps, getting there not only by car, but also by off-road vehicle, is not very easy. Needless to say, modern jeeps - “SUVs” are absolutely not suitable for hunting. Hunters, who have enough money, buy Hummers and Land Rovers, but even cars of these brands are often hopelessly stuck in forests and swamps.
Many self-tuning their cars, turning them into real "rogues." This procedure helps to increase the permeability of the car, however, this is not enough. There is a specialized class of vehicles, which can be attributed to the group of all-terrain vehicles. These cars have tracks instead of wheels, and pass on almost any road, or rather no roads. Unlike tank vehicles, these vehicles are fairly lightweight, which helps them overcome such obstacles, where a massive tank will definitely get stuck. One of these universal crooks is the tracked all-terrain vehicle GAZ-47.
How did the all-terrain vehicle GAZ-47
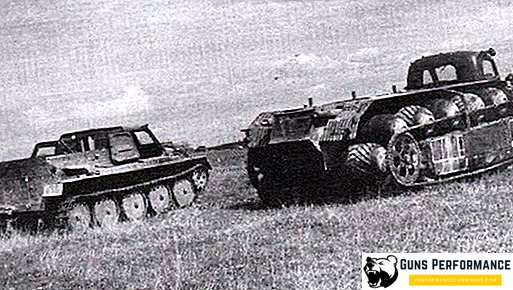
The Great Patriotic War clearly demonstrated that the patency of tracked vehicles is almost limitless. Having no experience in the development of this kind of all-terrain vehicles, the Soviet geological industry increasingly insistently demanded that a special all-terrain vehicle be created for it, which could reach any remote corner of the country.
In the 1950s, the leading design bureaus of the USSR began to develop tracked all-terrain vehicles, as the large-scale development of the northern regions of the country began.

The Gorky designers managed to produce the first model of the swamp in 1954. This model was tracked and was named GAZ 47 (GT-C). This model had:
- Tracked tank platform (borrowed from light tanks T-60 and T-70);
- Cab for the driver and passengers, which was located in front;
- Separate compartment for the engine;
- Roomy cargo bay.
Model GAZ-47 was made until 1967.
Features of the first tracked all-terrain vehicle of the USSR

Although the designers of the Gorky plant took about three years to develop an all-terrain vehicle, this time was not wasted. Gas-47 received outstanding performance in terms of patency. In order for the all-terrain vehicle not to get stuck in the swamp, in addition to reducing weight, the all-terrain vehicle received wide tracks. This feature allowed the technology does not sit on the "belly" and confidently leave any swamp.
The reduction in mass and the use of wide tracks made it possible to achieve a huge difference in pressure on the soil compared to the tank, on the basis of which the all-terrain vehicle was made. If the tank pressure on the soil is about 1 kg / cm, then the designers of GAZ-47 were able to achieve an incredible 0.2 kg / cm. These characteristics allowed not only to move confidently through the marshland, but also made it possible to drive through deep snowdrifts.
Another feature of this all-terrain vehicle was the ability to overcome water obstacles to a depth of 1.2 meters. In this mode, the GAZ-47 could easily drive 1.5 kilometers. There were attempts to install instead of the tracks special augers-floats, but such a modification of the all-terrain vehicle immediately lost its main quality - the ability to move to impassable places (and in general, in some places other than water).
In order for the all-terrain vehicle to get ashore, a rather gentle slope (about 20 degrees) was needed. Since the car was wide enough, to overcome the turbulent river was not recommended. An all-terrain vehicle in water lost maneuverability, and if it was beaten overboard to the high bank, there was a danger of lurch and flooding.
ATV is able to overcome:
- Obstacles up to 60 centimeters;
- Ditches with a width of 1.3 meters;
- Steep slopes, up to 60 degrees slope.
When designing the all-terrain vehicle, the developers took into account that this model is intended for geologists who work in the taiga and the Arctic, so the all-terrain vehicle was distinguished by extreme reliability and simplicity of design. The operation of the all-terrain vehicle in Antarctica was able to confirm the reliability data of this vehicle.
As for maintainability, the Soviet tanks of the times of the Second World War differed in that they could be repaired in the field, using the minimum set of tools. GAZ-47 in this regard took over tank maintainability.
Main technical characteristics of all-terrain vehicle GAZ-47

Since the all-terrain vehicle perfectly manifested itself in the harsh expeditions, this model is widely used in the army, geological and construction industry. In the taiga, this all-terrain vehicle was used in logging. Since the Gorky plant could not cope with the influx of orders, the production of the first Soviet tracked all-terrain vehicle was established at several other defense enterprises.
GAZ-47 could be used for casting troops in remote areas. The design of the model allowed to place two people in the cabin and ten people in the back. In addition, there was an open area for the placement of cargo and equipment.
The engine GAZ-61, which develops power up to 85 horsepower, was chosen as the engine for the all-terrain vehicle. This engine was a six-cylinder, four-stroke. A few years later this power unit was replaced by a more modern model. The GAZ-71 engine was chosen as the receiver. It had more power, which made it possible to increase the maximum speed of the car (the old engine reached a maximum speed of 35 kilometers per hour on a hard road, 4 km / h on water and 10 km / h on a swamp or deep snow).

On the basis of the GAZ-47 all-terrain vehicle base, many different modifications were produced for military, industrial, commercial, geological and civilian purposes. Throughout all the years of production of this model, the work on the development of new modifications did not stop, the most successful of which were included in the series.












