In connection with the operation that the aerospace forces of Russia are conducting in Syria, the press increasingly mentions the use of an unusual type of ammunition - concrete-breaking or anti-bunker bombs. What are these bombs, what are they for and how are they different from other types of aviation ammunition?
The concrete bomb (BETAB) is a type of aviation ammunition used to destroy various shelters (mainly protected by reinforced concrete structures), as well as runways (runways) of airfields.
In essence, concrete bombs are a type of high-explosive aerial bombs, which are distinguished by thicker walls (usually made of high-strength alloy steel) and a special fuse. Concrete bombs have a large caliber: from 500 to 1 thousand kg (for example, the Russian bomb BetaB-500), sometimes even more powerful ammunition is used.
In the classic war, BETAB is used to destroy the enemy’s bunkers, his command posts, pillboxes, coastal batteries, and mine installations. However, concrete bombs are successfully used in the counterguerrilla war, which has been repeatedly proved by the practice of recent years.
In Afghanistan and Syria, the rebels use a powerful network of underground communications, which are sometimes located at a fairly decent depth. Afghan mojaheds actively used (and continue to do) natural caves for their bases and strong points. For many years, the Lebanese Hezbollah fighters have created an extensive network of tunnels on the Israeli border. Moreover, it is not just hastily dug holes in the ground, many of these tunnels are securely fastened, equipped with electricity and other utilities.
Concrete bombs are often used to defeat all of the above objects.
The heyday of these aviation munitions came at the end of World War II: Allied aviation used giant anti-bunker bombs (weighing up to 10 tons) to destroy the concrete shelters of Nazi submarines. After the appearance of nuclear bombs and advanced missile weapons, developments in this direction have become less relevant. However, in recent decades there has been a real "renaissance" of anti-bunker ammunition.
Now the development of anti-bunker ammunition is actively engaged in the United States, Russia and Israel.
There are two main types of concrete bombs. The first group includes the free fall BETAB, which is usually used from a great height. Due to this, ammunition is gaining great speed, due to which it can hit deep and well-protected shelters. The second group of concrete bombs include ammunition with jet boosters. They can be used for bombing from low altitudes. Often such bombs have a parachute that stabilizes the flight of the ammunition at a certain angle. Then the parachute is shot off and the jet engine turns on.
One of the directions of development of this type of aviation ammunition is the creation of cluster bombs with striking concrete elements. Such aerial bombs are especially effective against the enemy’s runways and make it possible to guarantee the destruction of the runway cover immediately over large areas. An example of such an aerial bomb is the Russian RBC-500U.
Improvement of unitary concrete bombs also continues. Much attention is paid to improving the ratio between the mass of ammunition and its cross section. In addition, research is being conducted on new materials for the hull.

American concrete bombs
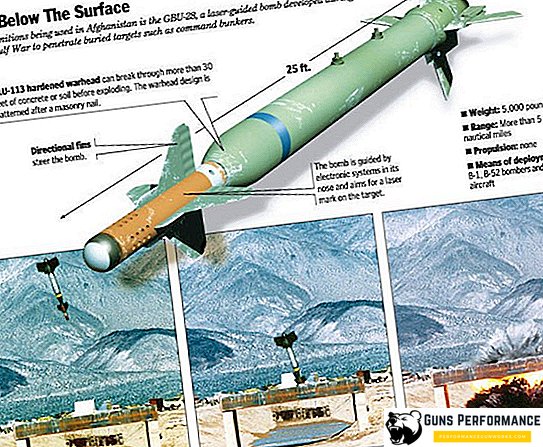
Currently, the most massive aviation munitions of this type in the United States is the BetaB GBU-28 (BLU-113). It was developed before the first war in the Persian Gulf specifically for the destruction of Iraqi military and government bunkers.
In order to effectively penetrate the ground and protective elements, the anti-bunker bomb must be heavy, have a small section and consist of a sufficiently strong material. The creators of the GBU-28 for a long time could not figure out how and from what to make its body. An excellent idea was suggested by a former army officer, he suggested making bombs from artillery barrels for 203-mm howitzers, which were stored in large quantities in military depots. They had the appropriate dimensions, had sufficient strength and weight.

During the test, the GBU-28 went underground at a depth of 30 meters. After the successful completion of the tests, the bomb was sent to Iraq and performed well in a real combat situation. Currently, this aerial bomb is considered one of the most efficient in the world in its class.

Another famous American BETAB is the BLU-109 / B. In addition to the United States, this bomb is used in the air forces of Canada, Belgium, Denmark, France, Saudi Arabia and other countries.

The BLU-109 / B is equipped with a time-delayed fuse, its warhead weighs 240 kg, and the total mass of ammunition is 907.2 kg. The bomb can be equipped with guidance systems Paveway III or JDAM. This BETAB is capable of piercing concrete floors 1.8 meters thick.
In early 2011, it was announced that the United States Air Force began operating a new anti-bunker "super-bomb" GBU-57, developed by designers of Boeing Corporation. It is quite comparable in size with the giants of the last world war: the weight of the GBU-57 is 13.6 tons, and the mass of the warhead is 2.7 tons. The bomb has laser guidance with GPS support.

Russian concrete bombs
The history of Soviet aviation concrete munitions began in 1940. It was then at GSKB-47 (today it is the SNPP "Bazalt") the development of the first Russian aviation concrete-breaking bomb began. The result of this work was the BetaB-150DS aerial bomb, which was used by Soviet aviation already during World War II.
BETAB-150DS was created on the basis of an artillery projectile of 203 mm caliber and contained 14.5 kg of explosive. This munition had a jet accelerating engine and could pierce the rock massif to a depth of 1.65 meters.
In the postwar years, work on the creation of new types of such ammunition was accelerated. Some aerial bombs, created in that period, are in service with the Russian Air Force today.
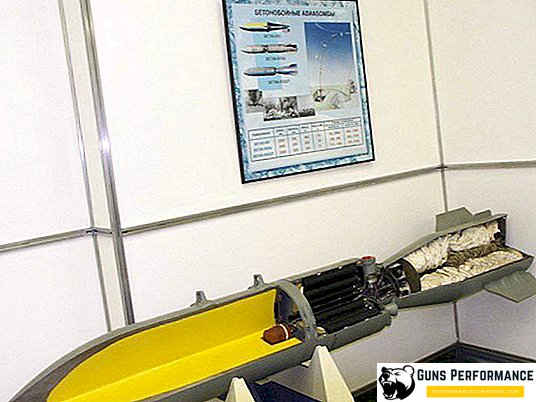

There are three types of anti-bunker bombs in service with the Russian Air Force: BetaB-500, BetaB-500U and BetaB-500ShP. They differ in size, weight and design. Also at the beginning of the 2000s, the RBC-500U cluster bomb was adopted, which contains concrete striking elements. The main purpose of the RBC-500U is the runway of the enemy's airfields.
BetaB-500U is a free-fall bomb that can be dropped from altitudes from 150 to 20 thousand meters. To ensure the optimum angle of collision with the surface, it is equipped with a drag parachute. The bomb is capable of breaking through 1.5 meters of reinforced concrete structures or 3 meters of soil.
BetaB-500U is used for the destruction of underground command posts or communication centers of the enemy, pillboxes, mine installations, ammunition depots and fuel and lubricants, reinforced concrete shelters of military equipment, and runways.
The mass of BETAB-500U is 510 kg, of which 45 kg is an explosive.
The concrete bomb BETAB-500 also belongs to free-fall ammunition. Its weight is 477 kg, the bomb carries 76 kg of explosive.
Another anti-bunker bomb, which is in service with the Russian Air Force, is the BetaB-500SHP. It refers to the assault jet concrete bombs. This bomb is equipped with a jet accelerator, so it can be used from a height of 170 to 1 thousand meters. Bombing is carried out in horizontal flight at a speed of 700-1200 km / h or from a dive with an angle of no more than thirty degrees.

BETAB-500ShP is primarily used to destroy the concrete pavement of the runways, it is able to pierce armor up to 650 mm thick or a layer of reinforced concrete 1.2 meters thick. The explosion of one such bomb can lead to uselessness of more than 50 square meters. meters of the runway. In addition to the Russian Air Force, the bomb BetaB-500ShP is in service with the Indian army.
In 2002, the RBC-500U cluster bomb was accepted into service by the Russian air force. It contains ten concrete-fighting elements and can be used at altitudes from 160 to 16 thousand meters. The main purpose of the RBC-500U are also airfield runways.
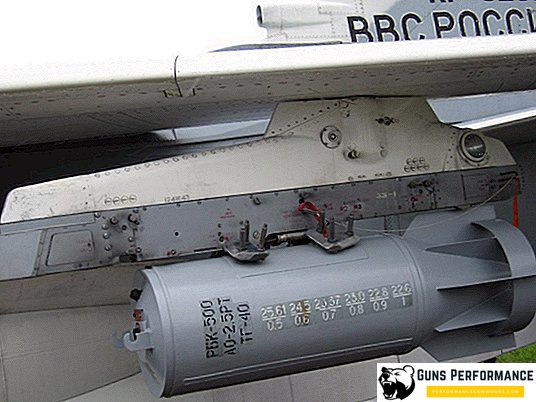

Israel
In early 2012, the new Israeli anti-bunker bomb MPR-500, developed by IMI, was introduced to the general public. The total weight of the ammunition is 270 kg, it can punch a layer of reinforced concrete with a thickness of up to one meter or penetrate through four concrete floors with a thickness of up to 200 mm each.
The high penetration capability of the bombs is caused not only by its considerable mass and strong body, but also by the jet accelerating engine, which creates acceleration of the ammunition immediately after it is dropped.
After the explosion, the MPR-500 air bomb gives more than a thousand fragments, which very effectively hit enemy enemy manpower at distances of up to one hundred meters.