The collapse of the Soviet Union put an end to the implementation of many interesting scientific and technical projects, most of which related to the military sphere. One of the most unusual Soviet developments was ekranoplanes - aircraft using the so-called screen effect for flight. According to the International Classification (IMO), these devices are classified as seagoing ships.
Such devices can be used for various purposes: for the transport of goods and passengers, the performance of rescue missions, sea patrols, but the Soviet ekranoplans were designed primarily for military needs.
The history of the creation of WIG in the USSR is associated with the name of a talented designer Rostislav Alekseev.
The result of many years of work by Alekseev and his subordinates was the creation of the Lun rocket WIG (project 903). Within the framework of this project, one device was built, although initially it was planned to manufacture eight WIGs. His main task was the destruction of aircraft carriers and other large enemy ships. In the West, "Lun" got the nickname "Caspian Monster". Most of the characteristics of this aircraft, no one has been able to surpass so far.

In the USSR, this project was absolutely secret, designers were forbidden to even utter the word "ekranoplan", in Western literature, such aircraft are designated by the abbreviation WIG (from Wing-In-Ground effect).
Due to what ekranoplan flies
The principle of flight of WIG is little similar to those used by conventional aircraft or hovercraft. The ekranoplan is maintained in the air also due to the airbag, but it is not injected by special engines, but arises due to the incident flow.
An ordinary plane takes off and flies, because the shape and profile of its wing creates pressure above its plane than under it. WIG is not like that. Due to air disturbances under his wing creates an area of high pressure, which reaches the surface and reflects back. This is the so-called screen effect. You can create it only at very low altitudes. It depends on the shape of the wing and its elongation, so the wing of the aircraft and the wig are very different.
The screen effect prevents pilots from carrying out maneuvers at low altitudes, but it is precisely this that forms the air cushion that keeps the ekranoplanes in the air. A similar effect strongly interested shipbuilders: first appeared ships on hydrofoils, and then the hovercraft. However, they both had maximum speed limits.
Rostislav Alekseev for many years engaged in the creation of ships on hydrofoils, his "Rocket" and "Meteora" did not have world analogues. However, this was not enough for the designer, and in 1961 he created his first ekranoplan.
History of creation
In 1967, the US military, studying the pictures taken by the spy satellite, discovered a huge flying machine in the Caspian Sea, which they immediately received the nickname “Caspian Monster”. In the future, this name was assigned to all Soviet devices of this type. What is so surprised American experts in the pictures?
They saw a real giant, a hundred-meter-long plane with disproportionately small wings — only forty meters. At the same time, the Caspian Monster could reach speeds of up to 500 km / h and moved at the height of the enemy’s uncontrolled air defense. Naturally, all this greatly puzzled Pentagon experts.
In 1967, a special meeting was held at the CIA to discuss intriguing satellite imagery. Experts from NASA and the military were invited to it, most of whom considered an amazing aircraft to be the focus or trick of the Russians, and only a few engineers came to the conclusion that they were dealing with a new type of aircraft.

In the photographs, the Americans saw the first large-scale creation of Alekseev, the ekranoplan called "Ship-Layout" or "KM". Its flight weight was 544 tons, and its wing area was 662.5 m2. On this machine, the Soviet designers worked out technical solutions that they planned to use when building serial WIGs.
In 1972, the first serial ekranoplan "Eaglet" was launched, the weight of which reached 120 tons. The “Eaglets” belonged to a new type of aircraft, the EK, during the flight they could use the screen or fly like a normal airplane. The Eaglet was able to deploy paratroopers over a distance of 1,500 km. Initially they planned to build 24 WIGs of this type, but only five cars were made.

In the course of the project, the designers were faced with a number of complex technical tasks related to the fact that the EKV had the features of both ships and aircraft. Lightweight materials were needed that could withstand corrosion and withstand the impact of water at a speed of about 500 km / h. In addition, the technique of piloting WIG very different from the aircraft.
In 1983, the Volga pilot plant laid the first rocket ekranoplan of the project 903 Lun. In 1986, his apparatus was launched, the tests began in the same year.
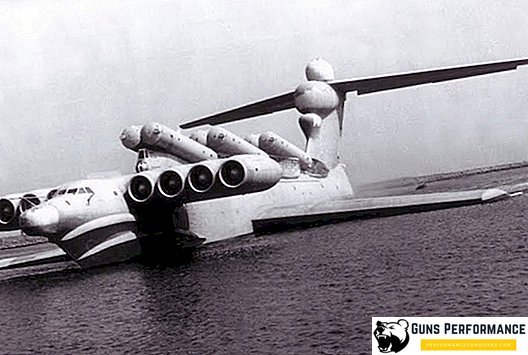
"Lun" was armed with six anti-ship cruise missiles "Mosquito", hitting at least one of them and today is fatal for almost any ship. The speed of the wig of the project 903 was 500 km / h.
In 1990, "Lun" was put into trial operation, and a year later he was removed from it and mothballed. Initially, they planned to build eight rocket WIGs of the project 903 "Lun", but they were not implemented. The reason for this was the difficult economic situation in the country and the recognition of the military inexpediency of using such devices.
The only ekranoplan of the project 903 "Lun" is preserved in dry dock today in the territory of the Dagdizel plant (Kaspiysk). All electronics has been removed from it.

After the collapse of the USSR and the cessation of funding, the second ship of the Lun project was wanted to be turned into a search and rescue, they were given the name “Rescuer”. He was supposed not only to conduct rescue operations at sea, but also to have a hospital for 150 people on board. Despite the 75% readiness of the "Rescuer", it was never completed.
The further fate of the already built Wile "Lun" and the entire project as a whole remains rather vague. In 2011, representatives of the Russian Ministry of Defense announced their decision to completely abandon the development and construction of ekranoplans. At about the same time, information appeared in the media that Rescuer and Lun plan to make part of museum exhibits, but there is no funding for transporting cars.

In 2018, several high-ranking officials announced at once that Russia would resume the construction of EKP shock screens. According to the announced information, the work should start in Nizhny Novgorod after 2020. In the same year, it was announced the completion of the draft design of the new naval wig A-050 with an take-off weight of 54 tons.
In August 2018, the Russian military department set a task for designers to create a car with a loading capacity of 240-300 tons by 2020. However, given the current not too brilliant position of the Russian economy and the sequestration of the defense budget, the future of ekranoplans cannot be called a cloudless one.
Description of construction
The ekranoplan "Lun" is made according to the monoplane's airplane scheme and has a trapezoidal wing located in the center of the hull. In the front part is the cockpit, there is also installed a pylon, on which are located eight NK-87 engines. The body of the ground effect vehicle is completely made of magnesium-aluminum alloy, which significantly reduces the weight of the "Lun" and reduces the likelihood of corrosion. The thickness of the skin is from four to twelve millimeters.
On the upper part of the body are six containers for anti-ship cruise missiles "Mosquito".
In the stern of the wig is the tail, which has a T-shaped.
The length of the hull "Lunya" is seventy-three meters, it is divided by partitions into ten waterproof compartments, and also the hull of an ekranoplan is divided into three decks. Bottom on the case is installed a ski device used during landing and take-off of the device.
The wing span is 44 meters, and an end washer is installed at its ends. The wing is waterproof, it houses four tanks with fuel.
The crew of the wig consisted of seven officers and four midshipmen. Autonomy "Lunya" - five days.
The power plant of the ground-effect vehicle (EKP) consisted of eight engines NK-87, its power was 104 kgf (8 x 13000).

The advantages and disadvantages of the project
It is not very correct to talk about the merits or shortcomings of the Eunoplanes of the Lun project, because all the features of this type of apparatus are inherent in it. The military has always been confused by the low defenses of WIG, which made it very vulnerable to enemy fire. Its speed is comparable to the speed of a low-speed aircraft, and the lack of anti-aircraft weapons made WIG easy prey for enemy aircraft.
- The undoubted advantages of WIG should include an excellent combination of speed and capacity. They can move with the speed of the aircraft (up to 600 km / h), while their carrying capacity is comparable to a small ship.
- The ekranoplans are very tenacious; in the event of an accident, they can simply land on the water, even with relatively high agitation.
- Such devices are capable of flying not only over the water surface, they are suitable for any flat surface: desert, tundra, ice.
- Ekranoplans are very economical: during the flight on the screen, they spend 30% less fuel than traditional aircraft.
- These devices do not need an airfield, just a small water area or a flat stretch of land.
- Another advantage of the wig is its stealth for radar as a result of flying at a height of several meters.
However, this type of aircraft has serious drawbacks, which greatly complicate their operation.
- The main one is that WIG cannot fly over an uneven surface, in this case it is impossible to create a screen. But, the truth is, there are no such flaws in the screen (Eaglet-type), which can fly like an airplane.
- Ekranoplans have very low maneuverability, they have a large turning radius.
- Despite being more economical than airplanes, a ground-wing wig must have a very high thrust ratio for take-off, which requires installation of take-off engines on it that do not work during the flight.
- The management of WIG requires special skills and is very different from piloting an airplane.

What's next?
Despite a number of shortcomings, the flight pattern using the screen effect looks very tempting. The impressive lifting capacity of the wig-rods makes these vehicles an ideal transport ship, capable of carrying people and cargo over ocean expanses.
Soviet ekranoplans simply had no luck: a number of offensive and non-obligatory accidents, a change of leadership, the disintegration of the state put an end to this potentially very interesting project. Alekseev planned not only to create huge shock and amphibious vehicles, but also to use WIG as a floating aircraft carrier and even a spaceport. This was not to be.
At the beginning of this century, the company Boeing was engaged in the project to create a Pelican airplane, which must carry 1,400 tons of cargo over a distance of 16 thousand km. The last mention of these works refers to 2003.
Work is underway to create such devices in Germany, France, China and South Korea. However, we are talking about small cars, with a maximum carrying capacity of several tens of tons.
Small ekranoplans are being developed today and in Russia.
Specifications
| Wingspan, m | 44,00 |
| Length m | 73,80 |
| Height, m | 19,20 |
| Wing area, m2 | 550,00 |
| Maximum takeoff weight, kg | 380000 |
| Engine type | NK-87 |
| Traction | 8 x 13000 kgf |
| Maximum speed, km / h | 500 |
| Flight altitude on screen | 1-5 m |
| Seaworthiness, points | 5-6 |
| Crew, pers. | 10 |
| Armament: | 6 PUKKR ZM-80 Mosquito |












