What is the essence of the greenhouse effect and what is its danger? Is it possible to stop global climate change, and how to do it?

Of the many problems facing modern humanity, climate change is undoubtedly one of the most significant and serious. Global warming, a rapid decline in biodiversity, the greenhouse effect, the melting of glaciers, which lead to a rise in the level of the oceans, can all have disastrous consequences and make the life of people on the planet simply unbearable.
Scientists warn that the climate problem can no longer be shelved: by 2030, the damage to the planet's ecosystem will be irreparable. That is, you and I have only 12 years left. If in the near future people will not find a solution to this problem, then the consequences of warming up the atmosphere will be felt for centuries, and even millennia. And this is not a question of ecology, but the survival of humanity. Why is it getting hotter on our planet? Blame the effect of the greenhouse effect, which arose as a result of human activities.
Some theory or why the planet warms up?
The greenhouse effect is the heating of the lower layers of the Earth’s atmosphere, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of certain gases in it. Its essence is quite simple: the sun's rays heat the surface of the planet, but at the same time, heat remains and cannot return to outer space - gases interfere with this. As a result of these processes, the temperature of the planet increases.
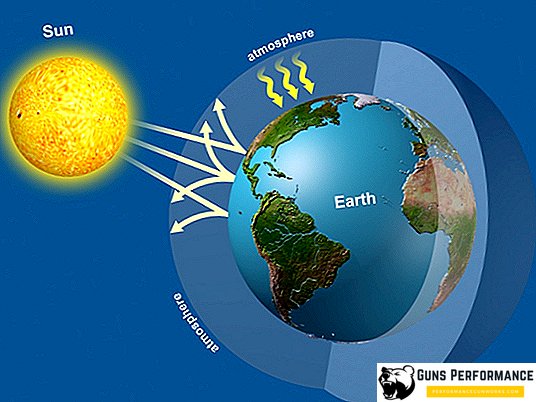
A significant proportion of solar radiation (up to 75%), falling on the Earth, falls on the visible and near-infrared part of the spectrum (400-1500 nm). The atmosphere practically does not catch it, and thermal energy freely reaches the surface of our planet. The Earth, heating in turn, begins to emit radiation with a wavelength of 7.8-28 microns, which is emitted into space, contributing to the cooling of the planet. The main cause of the greenhouse effect is a higher atmospheric transparency for light in the optical range than in the infrared. The fact is that some gases contained in the air absorb or reflect the radiation that comes from the Earth. They are called greenhouse. The higher their concentration, the more solar heat remains in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases disrupt the heat balance of the planet, which largely determines its climate.
The essence of the greenhouse effect is well known to summer residents and gardeners, who have greenhouses on their plots. The scheme is very similar: the sun's rays, getting inside, heat the soil, and the roof and walls do not allow the heat to leave the structure. Therefore, in a greenhouse, even without any heating, the temperature is always higher than outside.
Now they talk a lot about global warming and climate change. There is an erroneous opinion that the occurrence of the greenhouse effect is an event of recent years or decades, and its cause is solely human activity. This effect is inherent in any atmosphere, and without it life on Earth would have been impossible.
In fact, our problem is the rapid increase in the greenhouse effect that has been observed in recent years. This process can lead to disastrous results.
The history of the study of this issue
The study of the problem of the greenhouse effect began in the first half of the XIX century. In 1827, Joseph Fourier's work “A Note on the Temperatures of the Globe and Other Planets” was published, where he examined in detail the mechanisms of climate formation, as well as the factors that affect him. This scientist first described the phenomenon of the greenhouse effect, using as a model a glass vessel exposed to sunlight. Glass is almost opaque to infrared radiation, so this experience fairly accurately demonstrates the essence of the phenomenon. The very concept of the greenhouse effect came into scientific use much later.
Later, these studies were continued by the Swedish physicist Arrhenius. It was he who advanced the theory that the decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is one of the most important causes of the ice ages in the history of the planet.

However, the active study of the greenhouse effect and the effects of this phenomenon began only in the second half of the last century. Scientists have studied the change in solar radiation flux that occurs when the amount of greenhouse gases in the air increases. Now, to simulate the processes occurring in the atmosphere, the most modern and advanced computers have been used. But their power is often not enough, because the planetary climate is an extremely complex and not yet fully studied system.
In recent decades, at the international level, the first serious steps have been taken to address this problem. In 1992, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change was adopted. In 1997, the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement (2015) were added to it. About this document regulate measures to reduce emissions.
Greenhouse gases and other causes of warming
Scientists believe that the greenhouse effect occurs due to the following gases:
- methane;
- carbon dioxide;
- water vapor;
- ozone.
The greatest contribution to the increase in global temperature is made by water vapor (from 36 to 72%), followed by CO2 (approximately 9-26%), followed by methane (4-9%) and ozone (from 3 to 7%). Other gases have extremely low concentrations in the air, so their influence on climate processes is minimal.

The amount of water vapor strongly depends on the temperature of the lower layers of the atmosphere. The lower it is, the lower the humidity and the weaker the greenhouse effect. In this case, excess moisture turns into a snow-ice cover at the poles of the planet, increasing its reflectivity (albedo) and making the air even colder. Thus, global warming (or cooling) is a self-sustaining process, which under certain conditions can go on increasing and develop very quickly. To start it you just need a "trigger", and the anthropogenic factor may well become them. In this case, we are dealing with a typical example of positive feedback.
The periods of warming and cooling that had previously occurred on our planet perfectly correlate with the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Its increase leads to increased greenhouse effect and prolonged increase in temperature.
In addition, the soot and solid aerosol particles entering the upper atmosphere also affect the heat balance of the Earth. Their main sources are volcanic activity and industrial emissions. Dust and soot interferes with the penetration of sunlight, which reduces the temperature of the planet.
Where do greenhouse gases come from?

Currently there is a consensus among scientists that current climate change is associated with an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and the greenhouse effect - a consequence of this process. And the warming has been happening for a long time. The main reason for increasing the greenhouse effect is human activity, which has become a powerful planetary factor. Since the beginning of the industrial revolution - that is, over the past 250-300 years - concentrations of methane and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere have increased by 149% and 31%, respectively. Here are the main sources of greenhouse gases:
- The rapid growth of industry. The main source of energy for our plants, factories, vehicles is fossil fuels - oil, natural gas and coal. As a result of their use carbon dioxide is formed, which increase the greenhouse effect. About half of the gases produced in the course of human economic activity remain in the atmosphere, the rest is absorbed by the ocean and terrestrial vegetation. Every year the population of the Earth increases, and, therefore, it requires more and more food, industrial goods, cars, which leads to an even greater emission of carbon dioxide, so the phenomenon of the greenhouse effect will increase. And if over the past century the temperature has risen by 0.74 degrees, then in the future scientists predict a growth of 0.2 degrees for each decade;
- Deforestation and agricultural development. Another major reason for increasing the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is the massive destruction of forests. In the process of photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, being a natural regulator of greenhouse gas concentrations. Deforestation is needed primarily to obtain new arable land in order to feed the rapidly growing human population. Agriculture also adds its contribution to the increase in global temperature. Livestock is associated with the formation of a huge amount of methane, which surpasses carbon dioxide in its greenhouse properties;
- Landfills Population growth is expected to increase waste. Today, landfills are occupied by vast territories occupying thousands of hectares. Each of them emits tens of thousands of cubic meters of methane and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. An effective solution to this problem does not yet exist - it means that the emissions of "garbage gases" will only grow.
What threatens the greenhouse effect?
The history of the Earth has about 4.5 billion years, and throughout this time the climate of the planet has been constantly changing. In some epochs, lush tropical vegetation covered it from pole to pole; in others, it was a ball covered with a multi-meter layer of ice. Compared with such cataclysms, a one or two degree rise in temperature seems to be a real trifle: you will think, we will also save on heating! But not everything is so simple, the consequences of climate change may turn out to be much more serious, here are just some of them:
- An increase in temperature will lead to the melting of glaciers and a rise in the level of the waters of the oceans, which threatens to flood large areas. Of course, the planet does not turn into a "water world", but many coastal cities and territories can suffer. Few people know, but since the beginning of the 20th century the ocean level has risen by 17 cm, and since the mid-90s this rate of ascent has increased to 3.2-3.4 mm per year. This problem is aggravated by the fact that most of the population of the Earth lives in coastal areas, there is also a significant proportion of the world economy;
- An increase in temperature will inevitably lead to changes in the distribution of precipitation, as well as their quantity. And this result is probably even more serious than the flooding of certain territories. In some areas of the globe, rains will become very rare, and they will gradually turn into deserts, while in others, residents will suffer from regular hurricanes, floods, tsunamis and other disasters. According to scientists, a further increase in air temperature will lead to lower yields of major crops in the tropical and subtropical regions of the planet, which can lead to hunger and social upheaval;
- Higher temperatures adversely affect people's health. Doctors expect an increase in the number of cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases and even mental disorders.
The greenhouse effect and its possible consequences will seriously affect not only humans, but also the ecosystem of the planet as a whole. Climate change will deprive many species of their usual range, and it’s not a fact that all “our smaller brothers” will be able to adapt to such dramatic changes. The disappearance of some species will break the usual food chains, which can lead to a real "domino effect." Increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and increasing the temperature of the air leads to acidification of the ocean, which negatively affects all who live in it.
How to deal with it?
Man has repeatedly experienced climate change. Moreover, they were one of the driving forces of historical progress. Droughts and floods more than once or twice caused wars and revolutions, mass migrations of peoples, the decline of states and entire civilizations. How to avoid those catastrophic consequences that await us in the event of serious climate change? Is there a chance to reduce the so-called greenhouse effect? What can be done for this?

Today we know all the factors that lead to the accumulation of greenhouse gases and an increase in air temperature. It will be very difficult to reverse the current trend, since it will require the efforts of all mankind and a radical restructuring of the global economy. For a start, you just need to understand that the greenhouse effect is a global problem that threatens not all states, but all people.
Experts believe that the following measures are necessary to reduce greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere:
- It is necessary to fundamentally rebuild the energy sector and reduce the amount of industrial emissions. The main source of CO2 today is the burning of fossil fuels: oil, coal and gas. To reduce them, humanity must switch to the so-called renewable energy: the sun, wind, water. In recent years, their share in the overall balance has been growing quite rapidly, but these rates are clearly not enough. We also need to abandon the use of cars with internal combustion engines and transfer to electric vehicles. It is clear that all of the above requires multibillion-dollar investments and dozens of years of hard work. But you have to start it today;
- Improving energy efficiency, and this applies to industrial production, and energy production, and housing and communal services. The energy intensity of the products must be significantly reduced. We need new technologies that would not harm the environment. Even elementary insulation of building facades, installation of modern windows and replacement of heating plants can have a significant effect in terms of energy savings, and, therefore, reduce fuel costs and reduce harmful emissions;
- A very effective way to combat the greenhouse effect is to reduce waste. A person must learn to use resources again, this will allow eliminating landfills, which are a serious source of methane, or at least significantly reduce their volume;
- It is necessary to stop the predatory destruction of forests and engage in the restoration of green areas. Felling must be accompanied by planting new trees.
The fight against the greenhouse effect and the growth of average annual temperature should be conducted at the international level, in close cooperation between different countries. The first steps in this direction have already been taken, and the movement must continue. Scientists propose to consolidate the fight against climate change at the level of the constitutions of states. The role of non-governmental organizations that constantly raise this topic is also great. We must clearly understand how small our planet is and how vulnerable it is to man.