Among the vast number of Soviet weapons and military equipment there are several samples, which without exaggeration can be called legendary and iconic. It was with them that foreigners associated the image of the Soviet army, which is able to reach the shores of the English Channel in a matter of days. In addition to the legendary Kalashnikov assault rifle and the famous Soviet tanks, this list can also include the Mi-24 combat helicopter, which has been in service with the Soviet and then the Russian army since the early 70s.
Mi-24 - Soviet attack helicopter, explosive mixture of attack aircraft and infantry fighting vehicle. This heavily armed, armored and incredibly robust helicopter was involved in many conflicts and perfectly proved itself to them. It was originally designed for the classic war in the European theater of military operations, but later it turned out that the Mi-24 is perfect for local conflicts and the fight against partisans. The Mi-24 helicopter (nicknamed “crocodile” in the army) is a true symbol of the Afghan war.
The Mi-24 attack helicopter has many modifications, and its production continues to this day. This helicopter is the second largest after the American helicopter AH-64 Apache. At the moment, the Mi-24 is in service with several dozen armies in the world, all produced 3.5 thousand units of this machine.
A bit of history
The history of helicopters began almost immediately after the end of the Second World War. The pioneers in this business were the Americans, the first rotorcraft were used during the Korean War. The first helicopters were piston, they were used for reconnaissance, target designation and evacuation of the wounded.

Military people are quite conservative, so at first the helicopters had many opponents. American generals did not like their low-speed, weak security and the lack of weapons. However, the experience of the fighting showed high efficiency of helicopters. For example, the use of helicopters to evacuate the wounded several times increased their survival.
By the end of the Korean conflict, the United States became the most "helicopter" country in the world; several dozen companies were engaged in the creation of such aircraft.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the collapse of the colonial system resulted in dozens of local conflicts around the world, in which usually regular troops confronted different rebel groups, often based in inaccessible areas. And then it turned out that the helicopter is a magnificent tool of the anti-guerrilla war.

In the mid-60s, a new military unit emerged in the United States - the airmobile division, which included more than 400 army helicopters. Immediately after the formation of the division was sent to the jungle of southern Vietnam. In 1966, the world's first attack helicopter, the AH-1 Cobra, appeared in the sky of this country. This machine was not supposed to carry troops or reconnaissance, its main mission was to destroy the enemy.

Another turning point in the biography of combat helicopters was October 1973. During the next Arab-Israeli conflict, 18 attack Israeli Cobra helicopters destroyed 90 Egyptian Soviet-made tanks during one sortie. In the West, they realized that the attack helicopter is the best anti-tank weapon.
In the USSR, they did not immediately see the potential of the new aircraft, but then excitedly rushed to catch up with potential opponents. In 1965, began the production of the famous multi-purpose helicopter Mi-8, which can be called a military transport. Guided missiles and a 12.7 mm machine gun were installed on it. The cockpit and engines were protected by armor. In addition, this machine could take on board more than twenty paratroopers.
However, the Soviet military needed a combat helicopter with more powerful weapons, capable of not only carrying troops, but also effectively destroying enemy manpower and military equipment. The development of a new attack helicopter began in 1967. The Soviet concept was different from the American. Designers needed to create not just a strike helicopter, but a flying infantry fighting vehicle, which could not only land the troops, but also, if necessary, cover it with fire.
The new helicopter was planned to be equipped with a GSh-23 aviation gun, unguided rockets (up to 120 caliber), Phalang anti-tank missiles, and air bombs (up to 500 kg).
The Mil Design Bureau and the Kamov Design Bureau participated in the tender for the development of a new car. Kamovtsy presented the Ka-25Sh helicopter (modification of the anti-submarine helicopter), Miles took a slightly different path.
By the time the competition began, the Mi-8 helicopter was already in mass production, all of its components had been worked out, and “childhood” diseases were eliminated. It was noticeable that the G8 had a high modernization potential. Therefore, it was decided to develop a new attack helicopter based on the Mi-8.
A new TVZ-117 engine was developed for the future helicopter, work began on the creation of a new-generation ATGM “Sturm”. Unlike the Phalanx, he had semi-automatic guidance and a high speed of a rocket. The case of the Mi-8 was compressed from the sides, the wings were installed on it, the gearboxes carrying the propeller and transmission were completely replaced. The wings created additional aerodynamic resistance, reducing the speed of the machine, but at the same time unloaded the screw, and it was possible to hang weapons on them. In the central part of the fuselage was the landing compartment, which contained eight fighters.
The chassis of the new army helicopter decided to make retractable. The aircraft gun was replaced with a four-barrel 12.7-mm machine gun, which made it possible to significantly increase the ammunition load.
The Ka-25SH turned out much lighter (7.5 tons), but it could either carry strike weapons or carry troops. However, this did not suit the military too much. “Flying” BMP Mile came to their liking much more: his car could not only deliver troops, but also suppress the enemy with fire. Mil OKB was the winner in this competition.
There is a legend that after the victory of Miles, in a private conversation with Kamov, he agreed on a kind of "division of labor": he promised not to be too zealous with orders from the Navy, and Kamov agreed not to "trap" into land orders.
The first experienced Mi-24 was created in 1969, the tests began. Leaders of the highest rank were interested in the work, and Brezhnev personally controlled them.

Tests revealed a number of defects that affected both the engine and armament systems, and the stability of the machine in flight. The military has a lot of complaints caused by the overall layout of the helicopter. Most of all criticism perepalo cockpit, for which immediately stuck nickname "veranda". She had a lot of glass, but despite this, the review of the crew members left much to be desired. The cockpit had a large number of straight edges, which gave numerous reflections that strongly interfered with the pilots. The cab's car doors also didn’t suit the customers too much.
The weapons control system did not work satisfactorily, but, despite all these flaws, the Mi-24 helicopter was put into mass production.
Helicopter modifications
The first serial modification of the helicopter was the Mi-24A. Its production began in 1971. The car had an elongated cabin, the side parts of which were covered with steel armor, and the commander of the crew also had armored backs. The armor was and frontal armored glass, side windows were made of plexiglass. Crew members could use body armor and helmets in flight.
Helicopter tail rotor was located on the right side, the attachment of anti-tank guided missiles was changed. A total of 250 units of this modification were manufactured.

Mi-24A had a very impressive arsenal of weapons. A 12.7-mm machine gun in a rotary installation was installed on the nose, it could also carry four Phalangh anti-tank guided missiles, unguided aircraft rockets and aerial bombs (up to 500 kg).
Mi-24D. This is the first modification of a helicopter with a cabin of a habitual for us look, the crew members were located in it in tandem. The cabins were isolated from each other, each of them had its own armored lantern, the commander left his cabin through the door, and the navigator through the hatch. The release of the car began in 1973, a total of 600 units of this modification were manufactured. On the Mi-24D for the first time used a device to protect the engine from dust, which greatly increased its life, they installed on the air intakes.

Mi-24V. This modification has become a landmark, it was on it that the new Sturm anti-tank missile system with the Rainbow guidance system was installed. Now the “crocodile” could confidently fight the enemy’s armored vehicles. Four anti-tank missiles could be installed on the helicopter, in 1986 their number was increased to sixteen.
Some elements of the fuselage and the right side of the tail boom were also strengthened. The helicopter's fuel system was also upgraded, now additional tanks were installed on the holders, and not in the cargo hold. It should be said that the modification of the Mi-24V has become the most widespread - just 1 thousand cars were produced, production continued until 1986.
In 1989, the production of the Mi-24VP modification began, this car had more powerful weapons, a fire control system and systems that allow the use of a helicopter at night. The Mi-24VP was even equipped with air-to-air missiles, which allowed it to shoot down enemy planes. It was released about 30 of these machines. According to experts, this model of the helicopter exceeded the American Apache helicopter in all its characteristics: speed, security, and combat power.

Mi-35 is an export version of the Mi-24V.
The war in Afghanistan has become a harsh test for the Mi-24. The weakness of this machine was the insufficient efficiency of the rotor. It was very important for the conditions of the Afghan highlands. To solve this problem should increase the engine power. The designers managed to bring the static height to 2.1 thousand meters.
Another serious problem was the lack of machine protection from man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS).
Automatic guns were installed on the helicopters to shoot off the heat traps, in addition, the LEPA SOEP station was installed on the Mi-24. Heaters and a system of mirrors located in its rotating head interfered with the GOS of missiles and significantly reduced the likelihood of a helicopter being hit.
Work was also carried out to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases of the engine. Special design mixed them with cold air, which reduced the temperature by 60%.
Another direction of modernization was to increase the combat effectiveness of the use of a helicopter. Uncontrolled aircraft missiles (NAR) S-5 were replaced by NAR S-8, surpassing them in all characteristics. Suspended containers with guns GSh-23A were developed. Suspended cassette containers filled with fragmentation, high explosive bombs or mines appeared. Holders were designed for eight high-explosive bombs FAB-100. A night sight was mounted on some helicopters, which expanded the combat capabilities of the vehicle.
Shortly after the outbreak of hostilities in Afghanistan, another helicopter version appeared - the Mi-24P, in which the YakB-12.7 machine gun in a mobile nasal installation, was replaced by a GSh-30K gun. The YakB-12.7 machine gun had excellent combat power, but its work (especially in the difficult conditions of Afghanistan) was extremely unreliable.
This is not a complete list of modifications of the famous helicopter, there are several dozen of them. Some of them were designed to perform special tasks (Mi-24R - reconnaissance, Mi-24K - fire spotter), some were experimental models that never went into the series. Part of the modifications was created specifically for export shipments.
An interesting modification of the Mi-24VM, which made its first flight in 1999. This helicopter was not planned to be mass-produced; rather, it was an attempt to overhaul the machines existing at that time. Mi-24VM received new rotors and tail rotors made of composite materials, a new gearbox without bearings, its steering screw got an X-shape. The helicopter landing gear was made non-retractable, which reduced the weight of the vehicle and increased the survival of the crew.
The engine power was also increased, the wing area was reduced, the range of weapons was significantly expanded.

The South African company ATE, in cooperation with Mil Millenium Design Bureau and Rosvertol JSC, created a modification of the Mi-24 Super Hind helicopter. Two more modifications South Africans created together with the Ukrainian plant "Aviakon". These cars were delivered to Algeria and Azerbaijan.
These helicopters are equipped with western navigation equipment, communications equipment and a fire control system. All this works according to NATO standards.
Work to improve the Mi-24 are underway today. JSC "Rosvertol" created several machines capable of effectively conducting combat operations at night. 14 helicopters were transferred to the Russian Armed Forces in 2004.
However, it should be noted that today the army helicopter Mi-24 is already an obsolete machine. And the point is not in its technical imperfection, but in the concept of its application. A heavy armored helicopter, poorly adapted for the use of precision weapons, is unlikely to be in demand in the future. The Mi-24 helicopter was developed more than forty years ago for a completely different war. Most of the shortcomings of this machine are solved on the Mi-28N, which, in fact, is an evolutionary development of the "crocodile".
Description of construction
The Mi-24V helicopter is the most massive modification of this machine. It is made according to a single-screw scheme, the bearing screw has five blades, the steering one has three. The crew of the helicopter - three people.
Two crew members (pilot and navigator) are in separate cabs, and the flight mechanic is in the cargo hold. At the first modifications of the helicopter, the crew consisted only of the pilot and the navigator. The cockpit of the pilot and navigator is completely sealed, they are provided with air conditioning system, which provides normal temperature conditions. There is an oxygen supply system, which is necessary for flights at an altitude above 3 km.
The pressure in the cockpit and in the cargo hold is slightly above atmospheric. This is done to prevent dust from entering or contaminated air.
The fuselage is a semi-monocoque, which consists of the nose and central parts, as well as the tail and end beams.
In front of the helicopter are the cockpits of the crew members: the pilot and the navigator-operator. The side walls of the cabins are armored, armored plates are part of the fuselage power circuit. The lights of both cabins are made of armored glass and plexiglass. The pilot's seat has an armored back and an armored headpiece. The door from the cockpit also has a reservation.
The cargo compartment is located in the central part of the fuselage, the seat of the flight engineer is also located there. There are double doors on both sides of the cargo hold. The height of the cargo compartment is only 1.2 meters, which makes it not very convenient for the transport of passengers.
The power plant is located above the cargo hold. It consists of two TV3-117V engines, a reducer, an additional power unit and a hydraulic panel. There is also a fan installation. Under the floor of the cargo compartment and in its rear part are fuel tanks. To the outer part of the fuselage in the cargo compartment fasten the wings of the machine. And below are the niches in which the side landing gear folds.
The tail boom has an oval section, inside it passes the transmission shaft. On the surface of the beam are rocket launchers, antennas, and flashing lights.
On the end beam there is a controlled stabilizer, a gearbox and a steering screw.
The wings of the helicopter are designed to create additional lift (up to 30%), as well as to install outboard weapons. They are set at an angle of -19 °.
The armament of the Mi-24V helicopter is outboard and small. The latter consists of a four-barreled machine gun YakB-12, 7, which is located in a mobile bow installation. In the horizontal plane, it can rotate + 60 ° from the longitudinal axis, rise by 20 ° and descend to 40 °.
The outboard armament of the helicopter includes various guided and unguided types of aviation weapons. Unmanaged include free-fall bombs, NAR, cannon containers. The Mi-24V helicopter can use bombs in caliber from 50 to 500 kg.
Controlled weapons include missiles of the Sturm anti-tank complex, which are suspended on external pylons and wing tips. This ATGM refers to the second generation of this weapon, targeting is carried out in a semi-automatic mode. A missile is aimed at a target by a navigator operator.
The power plant of the helicopter consists of two engines TV3-117V, auxiliary power unit and fan cooling system of the gearbox. Силовая установка имеет броневую защиту. Электрооборудование работает от двух генераторов, которые также расположены в силовой установке.
Топливная система состоит из пяти баков с общим объемом 2130 литров, которые оборудованы системой нейтрального газа и снабжены полиуретановыми вкладышами.
Несущий винт Ми-24В имеет пять алюминиевых лопастей со специальным наполнителем, которые вращаются по часовой стрелке. Несущий винт имеет наклон вперед 5% и влево - 3%, это улучшает устойчивость машины во время полета.
Шасси вертолета Ми-24 состоит из трех убирающихся опор, переднее колесо управляемое. Убирающееся шасси улучшает аэродинамические свойства вертолета и увеличивает его скорость, но добавляет конструкции лишние килограммы.
Combat use
Впервые в боевых условиях Ми-24 был применен в 1978 году в Сомали. Вертолеты пилотировались кубинскими летчиками и наносили удары по территории соседней Эфиопии. Машина хорошо зарекомендовала себя.
В 1979 году началась война в Афганистане, в которой Ми-24 принимал самое активное участие. "Крокодилы" оказывали огневую поддержку наземным войскам, уничтожали караваны с оружием, прикрывали советские колонны, совершали карательные рейды против афганских кишлаков и городов.
Ми-28 крайне редко использовался для транспортировки десанта, в основном он выполнял ударные функции. На первых порах повстанцам нечего было противопоставить тяжелым бронированным монстрам, несущим смерть с неба. Несколько машин было сбито с помощью зенитного огня крупнокалиберных пулеметов, но поразить Ми-24 было совсем не просто.

Ситуация изменилась после начала применения моджахедами переносных зенитно-ракетных комплексов, которые наводились по тепловому следу вертолетов. Особенно ситуация ухудшилась с появлением у повстанцев новейших американских ПЗРК "Стингер".
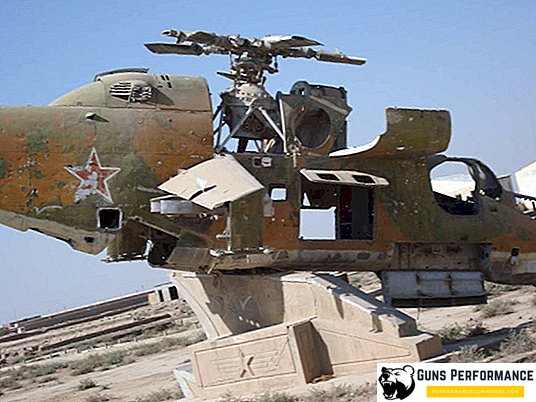

В 1989 году советские войска ушли из Афганистана. За десятилетие войны было потеряно около 160 вертолетов Ми-24 разных модификаций. Далеко не все они были сбиты противником. Много машин разбилось из-за крайне сложных условий пилотирования и эксплуатации. Всего же в Афганистане было потеряно 330 советских вертолетов различных видов.
В 1980 году началась ирано-иракская война, в которой также принимали участие Ми-24, состоящие на вооружении ВВС Ирака. Советским вертолетам приходилось не только выполнять ударные функции, но и бороться с американскими AH-1J "Си Кобра", которые оказались весьма достойными противниками.
После распада СССР "крокодилы" использовались практически во всех конфликтах, которые разгорелись в бывших советских республиках. В Нагорном Карабахе Ми-24 применяли обе стороны. Армянам удалось сбить шесть вертолетов противника, Азербайджану - один.
Во время конфликта в Абхазии российский Ми-24 сбил пушечным огнем Ми-24 ВВС Грузии.
Использовался этот вертолет и в Приднестровье.
Ми-24 активно применялся федеральными войсками во время первой и второй чеченской кампании. За время войны 1994-1996 гг. Россия потеряла 7 вертолетов Ми-24, во второй войне потери были гораздо больше - 23 машины (к 2005 году).
Ми-24 активно использовался во время балканских войн, в российско-грузинском конфликте (2008 год), а также в ходе гражданской войны в Сирии. В настоящее время этими вертолетами вооружены национальные армии Афганистана и Ирака, они применяют Ми-24 против талибов и игиловцев.
Украинские правительственные войска активно и весьма эффективно использовали Ми-24 на первых этапах конфликта на Донбассе. Потеряно четыре вертолета.

Ударные вертолеты Ми-24 активно использовались во время многочисленных конфликтов в Африке.
Advantages and disadvantages
Если говорить о достоинствах ударного вертолета Ми-24, то первое, что необходимо отметить - это его поразительная надежность и живучесть. Мощная броня, прикрывающая кабины пилотов и силовую установку, сделало этот вертолет практически не уязвимым для огня с земли. Эффективно поражать Ми-24 могло только крупнокалиберное оружие.
Еще одним неоспоримым преимуществом машины являлось ее мощное вооружение. С его помощью вертолет может решать любые задачи: эффективно уничтожать живую силу противника и его бронетехнику.
Ми-24 - это очень тяжелая и большая машина. Ее максимальная взлетная масса составляет 11500 кг (у американского АН-1 - 4500 кг). Для такого веса мощность силовой установки вертолета явно слабовата. Поэтому маневры и зависание - это не для "крокодила", его стихией является скорость.
На сегодняшний день устаревшей является концепция применения Ми-24. Грузовой отсек, в который должны были помещаться десантники, так никогда и не использовался по назначению, зато он здорово утяжелил машину.
Развитие современных вертолетов идет не по пути повышения броневой защиты (и, как следствие, увеличения массы), а в направлении более активного использования управляемого оружия, которое может поразить неприятеля на значительных дистанциях. В этом случае вертолету не нужно заходить в зону поражения ПВО противника и подвергать себя опасности. Однако для этого боевые машины должны обладать современной оптикой, системами прицеливания и управления огнем. Ничего этого на Ми-24 нет.
На Ми-35 и еще нескольких поздних модификациях вертолета от главных недостатков машины практически удалось избавиться, но модернизированных машин очень мало. К тому же, в настоящее время российская армия активно переходит на Ми-28Н.
Многие военные эксперты считают, что в недалеком будущем пилотируемые вертолеты будут заменены дистанционно управляемыми БПЛА. Они гораздо дешевле, да и людьми рисковать не нужно. Возможно, что Ми-28Н, Ка-52, как и их заокеанский аналог AH-64 Apache - это последние ударные вертолеты, управляемые пилотами из кабины.
Specifications
| Weight, kg: | |
| пустого | 8500 |
| normal takeoff | 11200 |
| maximum takeoff | 11500 |
| Длина полная, м | 21,35 |
| Wingspan, m | 6,66 |
| Диаметр несущего винта, м | 17,3 |
| Диаметр рулевого винта, м | 3,91 |
| Engine power, hp | 2х2225 |
| Скорость, км/ч: | |
| maximum | 320 |
| cruising | 264 |
| Статический потолок без учета влияния земли, м | 2000 |
| Динамический потолок, м | 4600 |
| Дальность полета, км: | |
| practical | 595 |
| перегоночная | 1000 |
| Масса груза, кг: | |
| normal | 1500 |
| maximum | 2400 |
| на внешней подвеске | 2000 |
| Crew | 3 |
| Число десантников, чел | 8 |
| Встроенное вооружение | пулемет ЯкБ-12,7 |
| ПТРК | 9К113 "Штурм-В" |